Induction Brazing Systems
Your Partner for Induction Brazing & Soldering
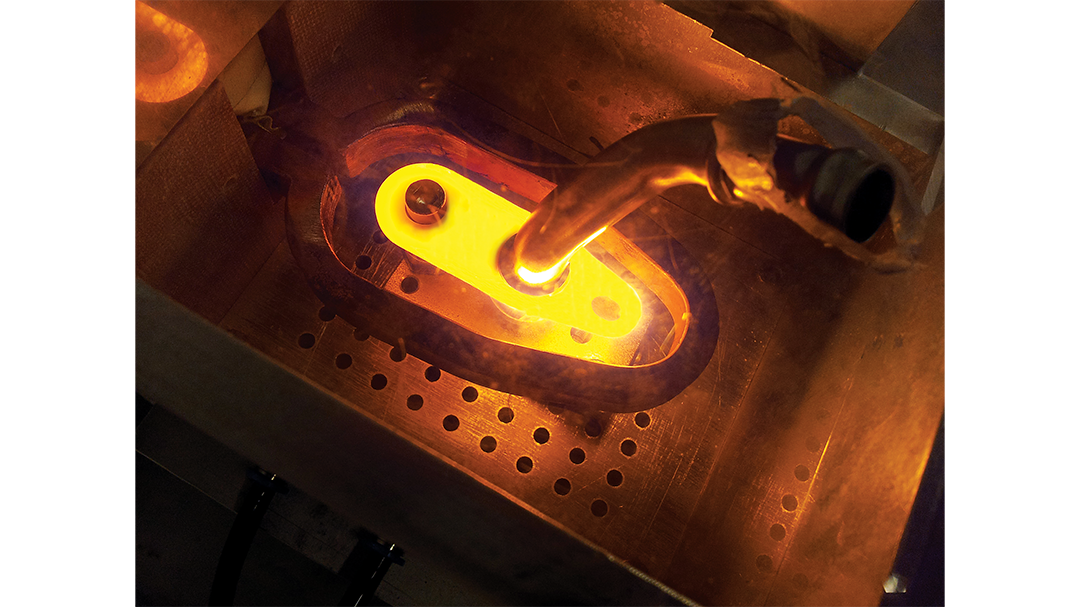
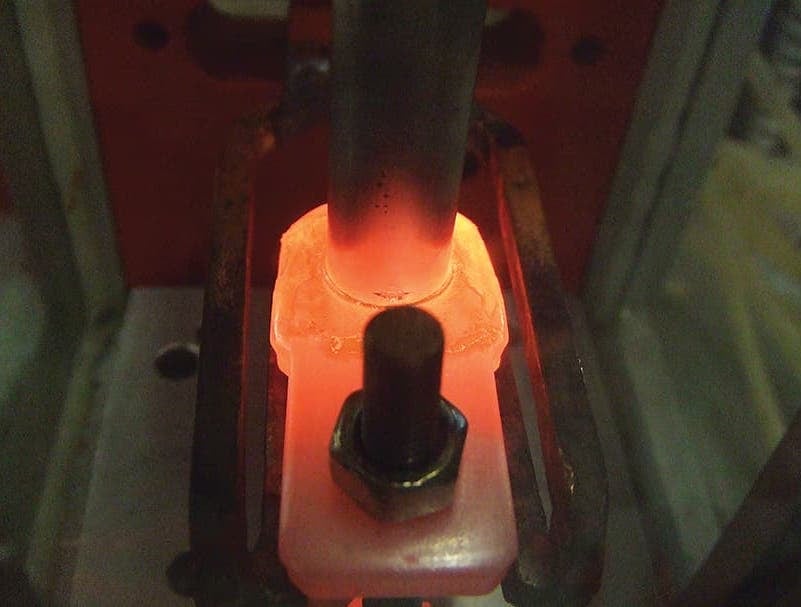
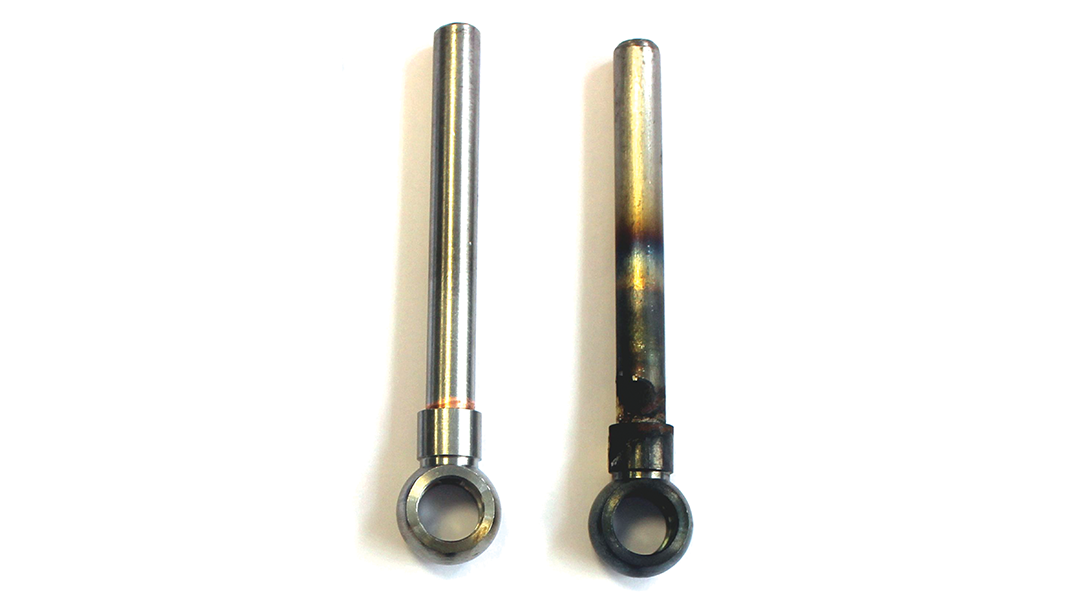
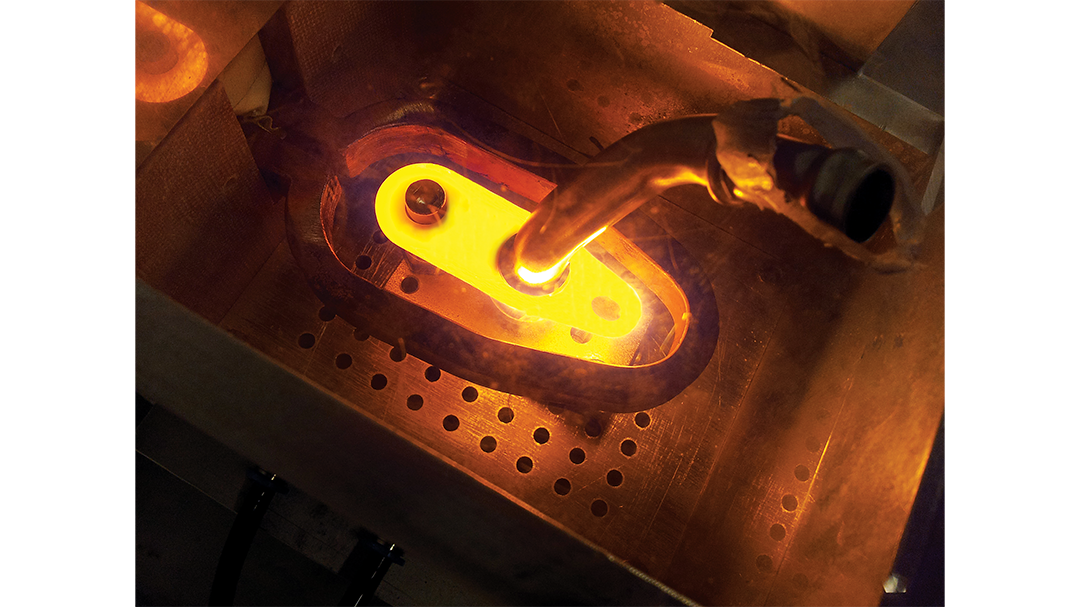
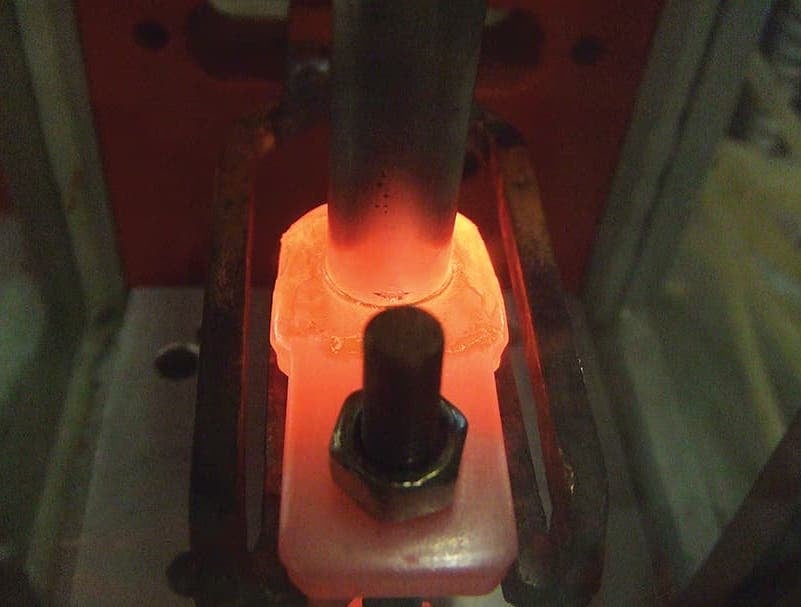
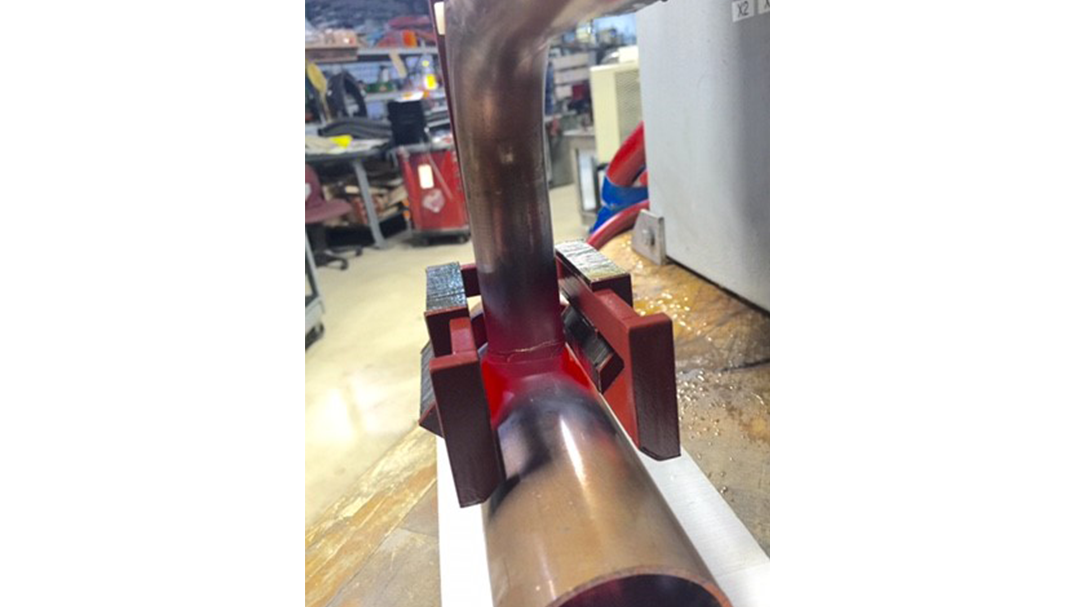
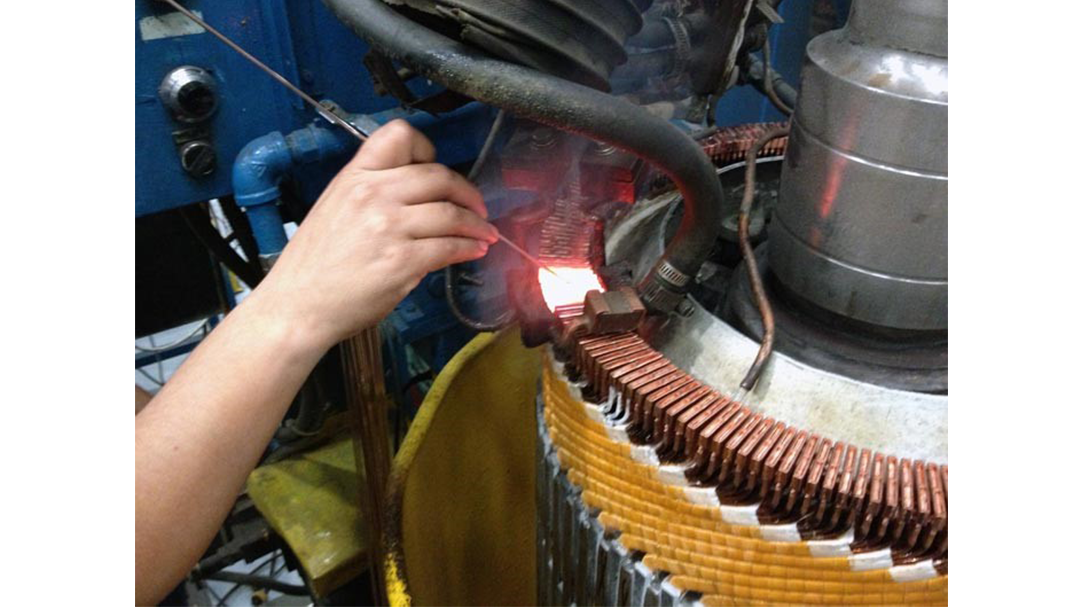
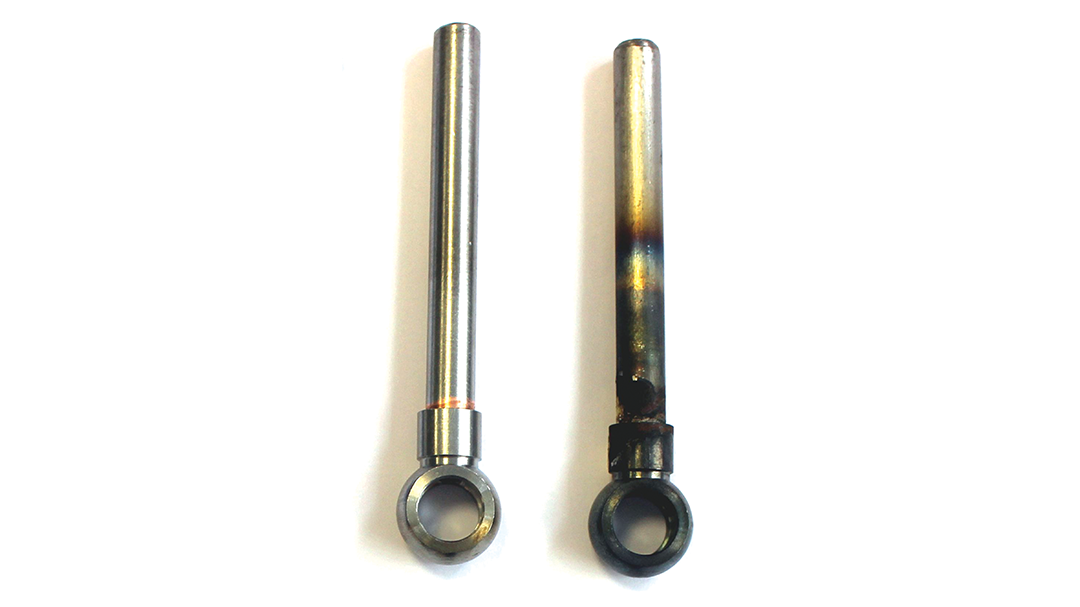
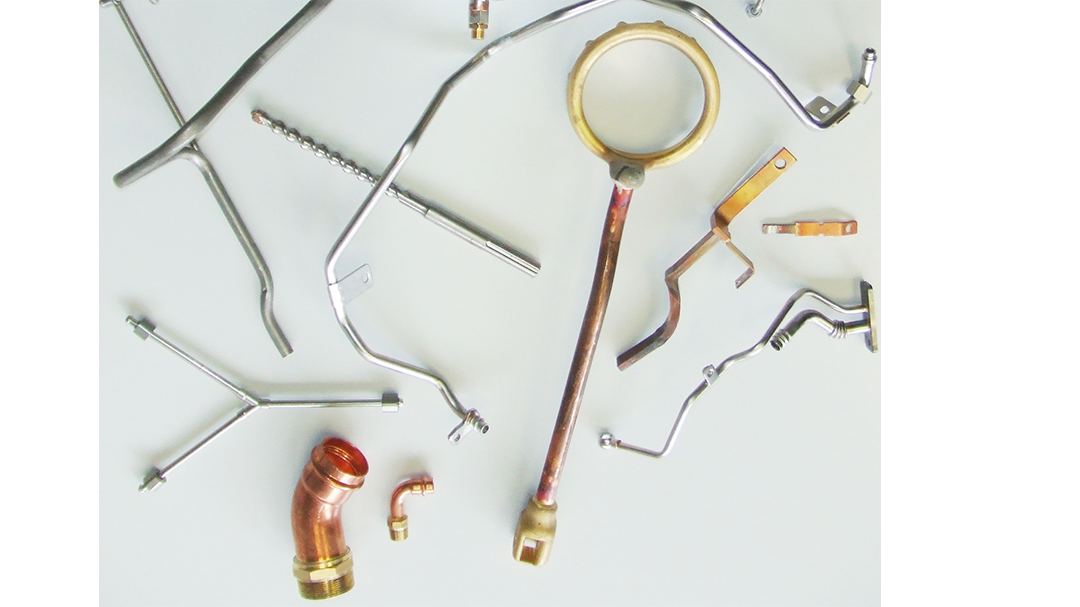
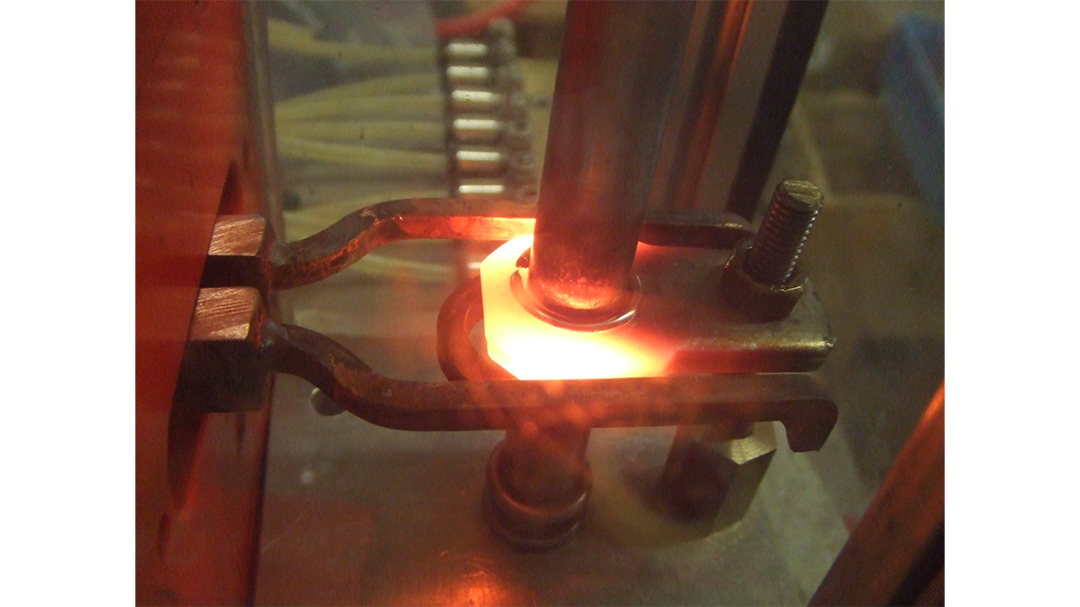
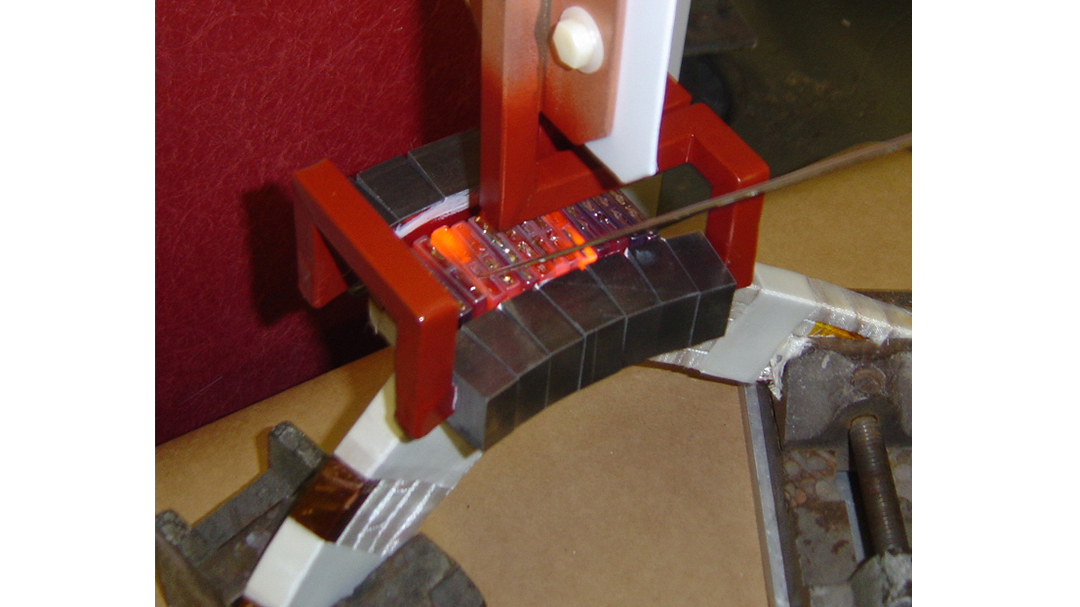
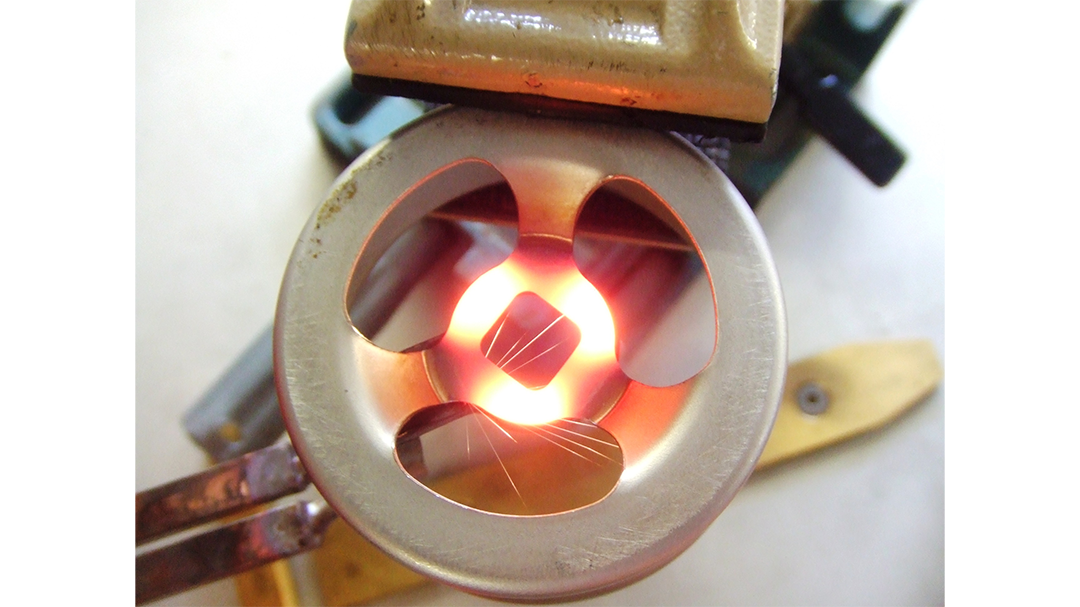
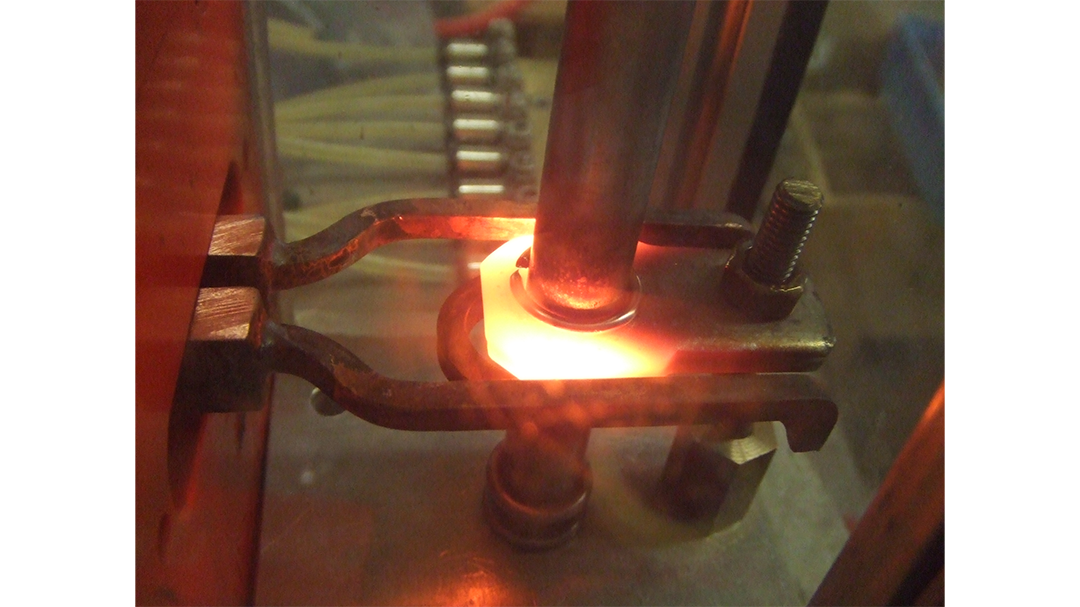
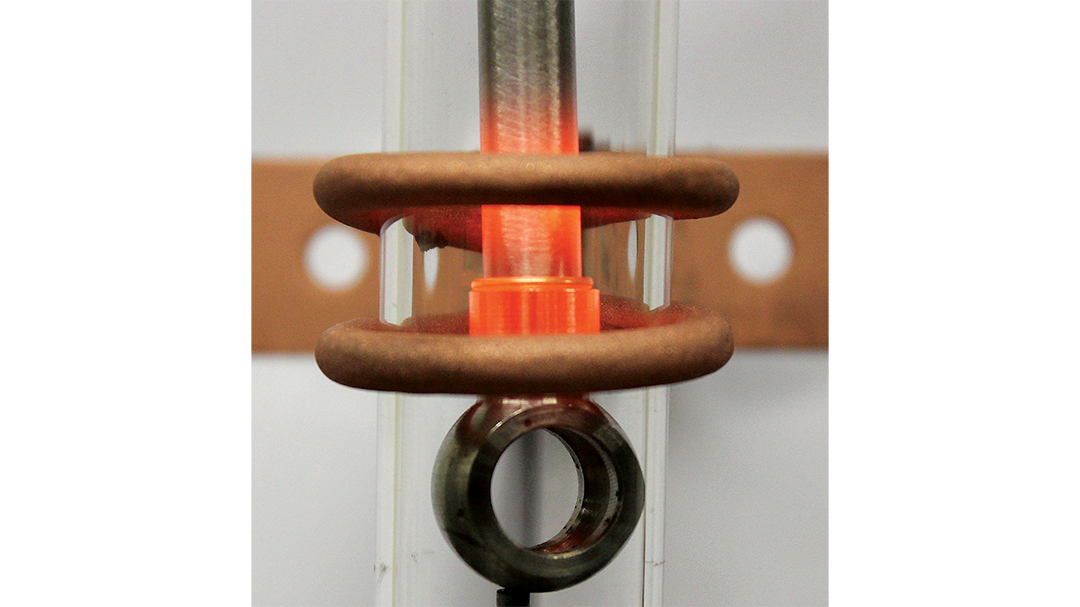
Induction brazing is a process of joining materials together using induction. An induction coil quickly transfers heat precisely to the joint, melting a compatible filler material through capillary action. Filler metals include lead, tin, copper, silver, nickel, and their alloys. Lead-tin soldering (soft soldering) is conducted below 840 degrees Fahrenheit. Silver brazing is conducted at temperatures from 840 to 1,600 F. Copper brazing is conducted at temperatures from 1,900 to approximately 2,000 F.
The success of these processes depends on chemical cleanliness, temperature control, and the clearance between the surfaces to be joined. Cleanliness is usually obtained by introducing a flux that cleans, dissolves, and floats off any dirt or oxides, however, fluxes should not be relied on as the primary cleaning agent in the process. Some filler metal and base metal combinations do not require the use of a chemical flux, such as when brazing copper base metals with a BCuP filler metal. The phosphorus contained in this filler metal family reacts with the copper base metals and reduces any oxides on the part. The flux also covers and protects the area by shielding it from oxidation during the process. It may, to some extent, reduce the surface tension of the molten metal to promote free flow. The worst contamination is usually due to oxidation during the brazing process. Many operations are conducted in a controlled atmosphere with a blanket of inert gas to shield the operation and eliminate the need for a flux. Temperature control, although influenced by fixture design, is dependent primarily on the heat application method.


















































Providing Heating & Melting Solutions Since 1916
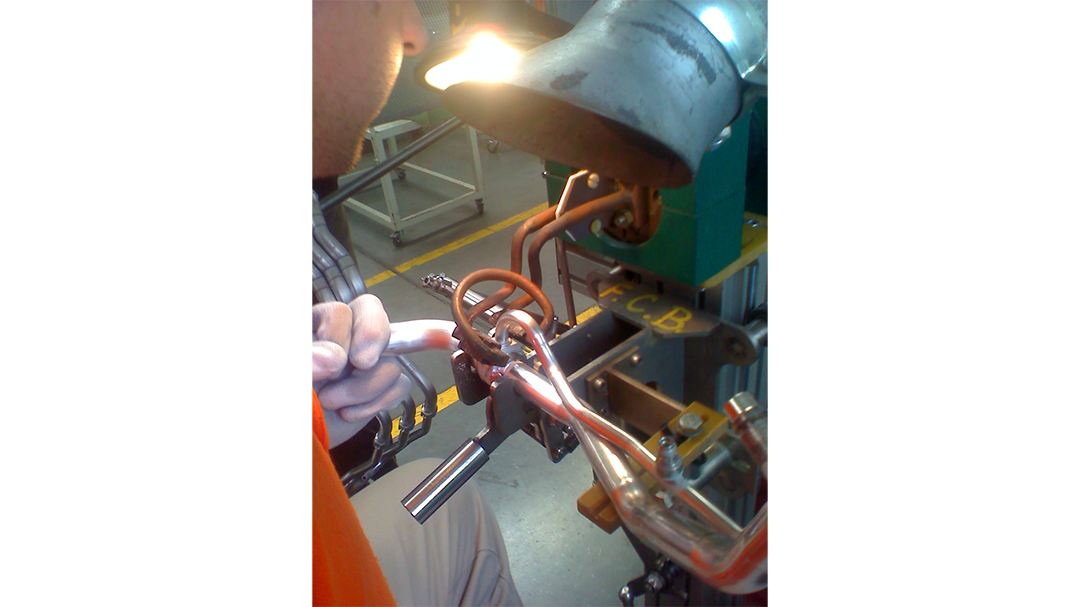
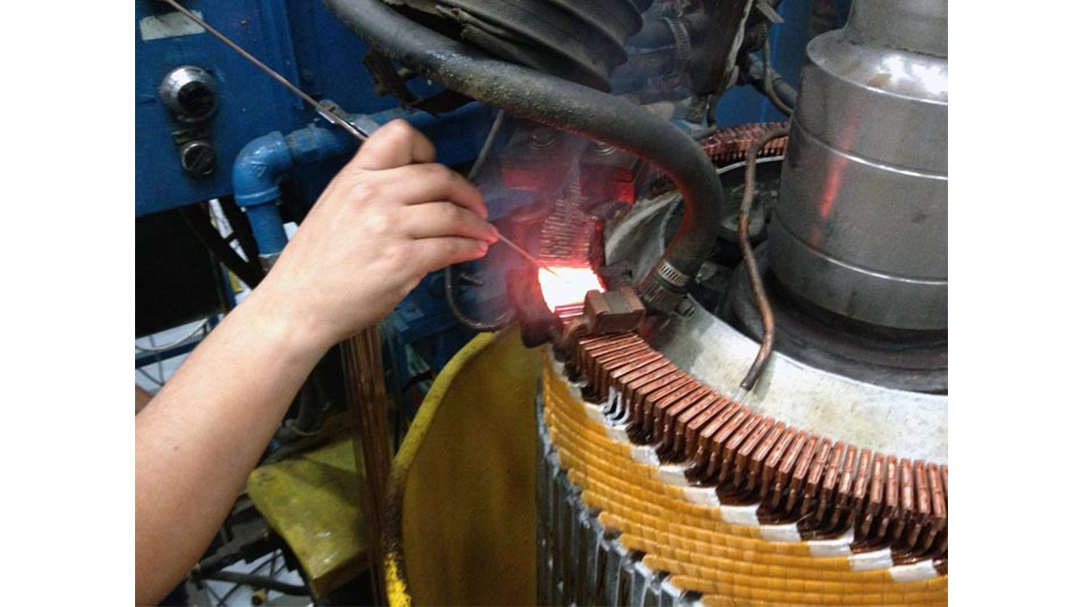
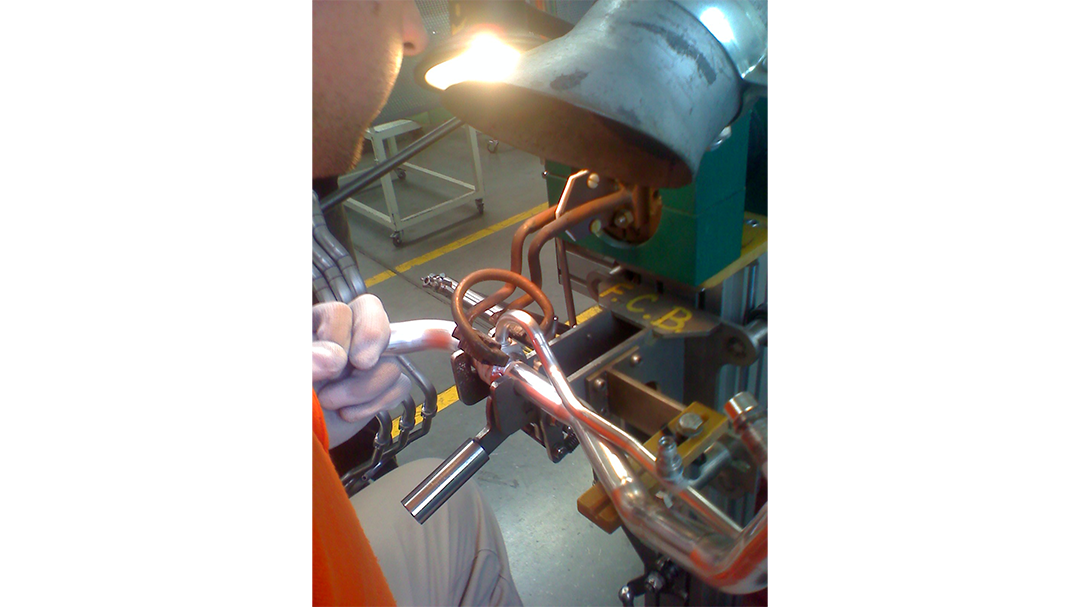
Replace the Torch With Induction
Many companies are making the switch from torch heating to induction brazing. Why? The main reasons are speed, safety, and repeatability. Induction provides a rapid, exact heat, meaning you can increase production and repeat the process over and over with the same even, predictable results with no open flame. The localized heating means less energy and better heat transfer to the area you need it, without heating other areas of the part.
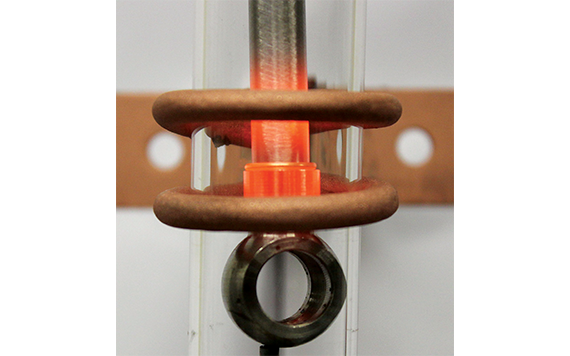
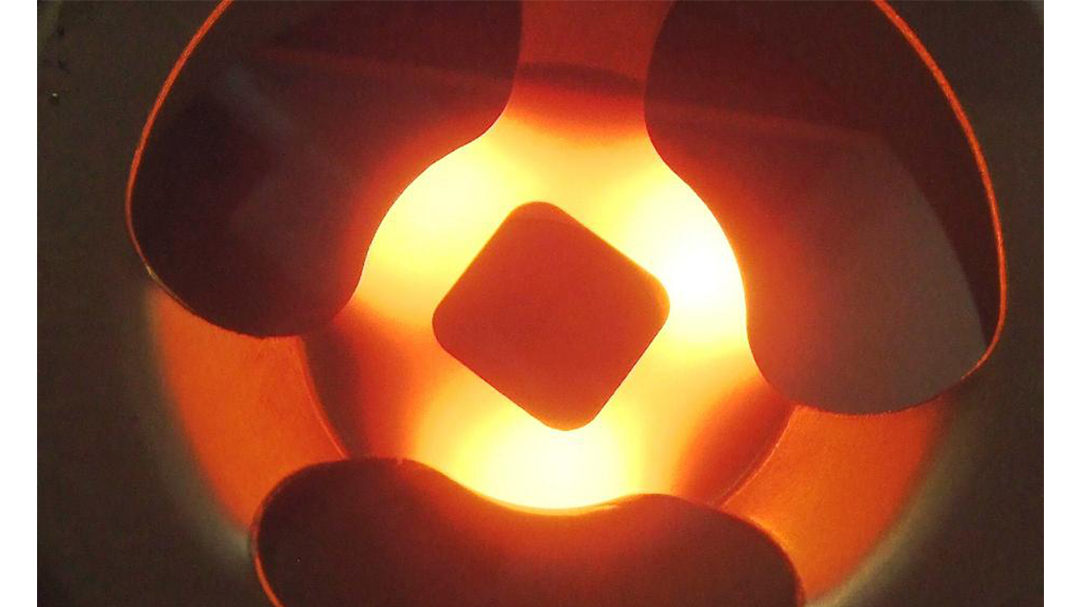
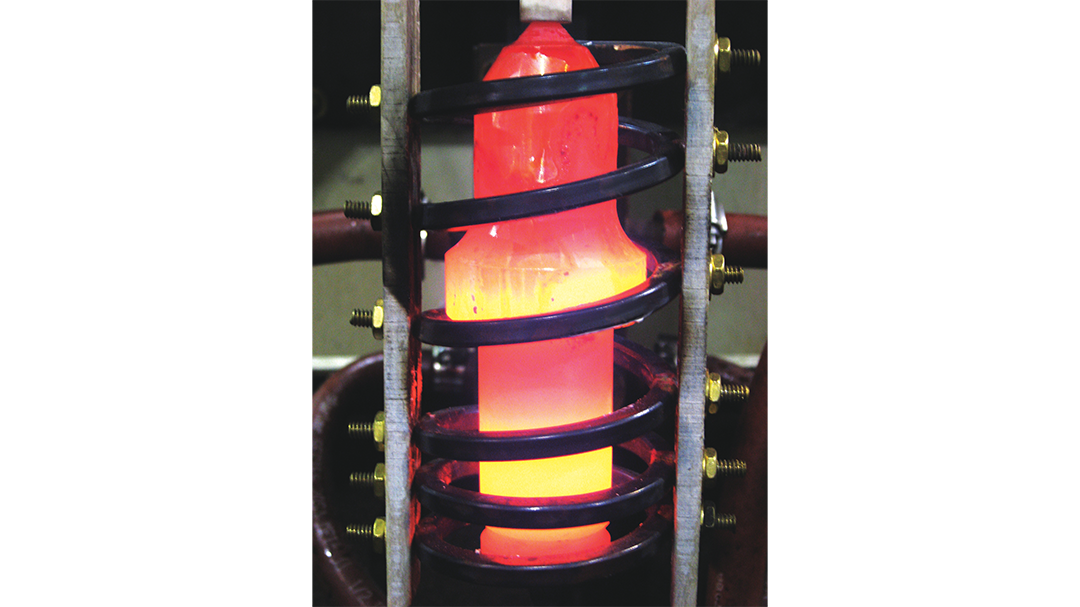
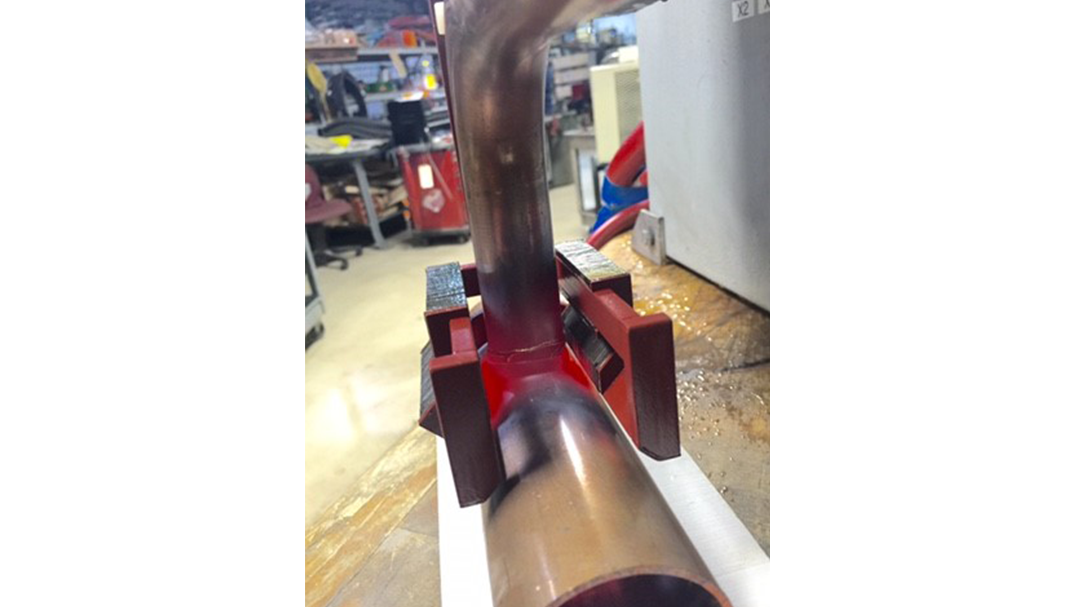
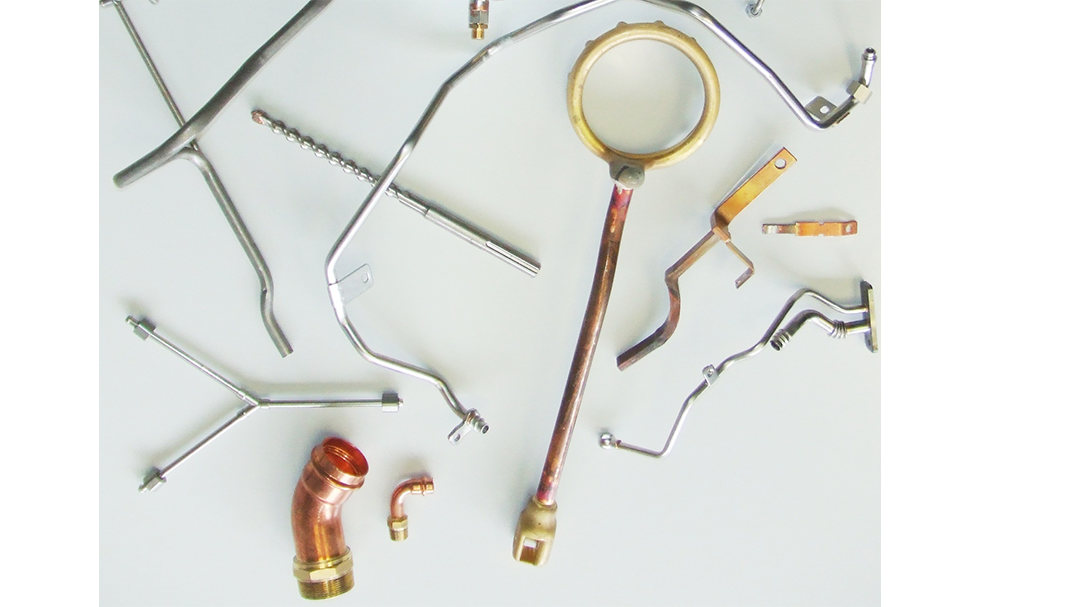
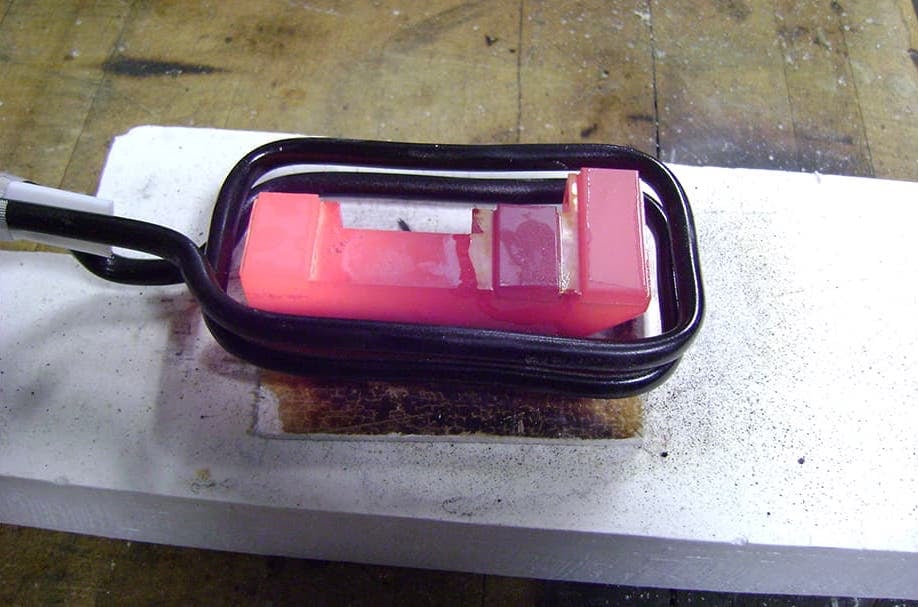
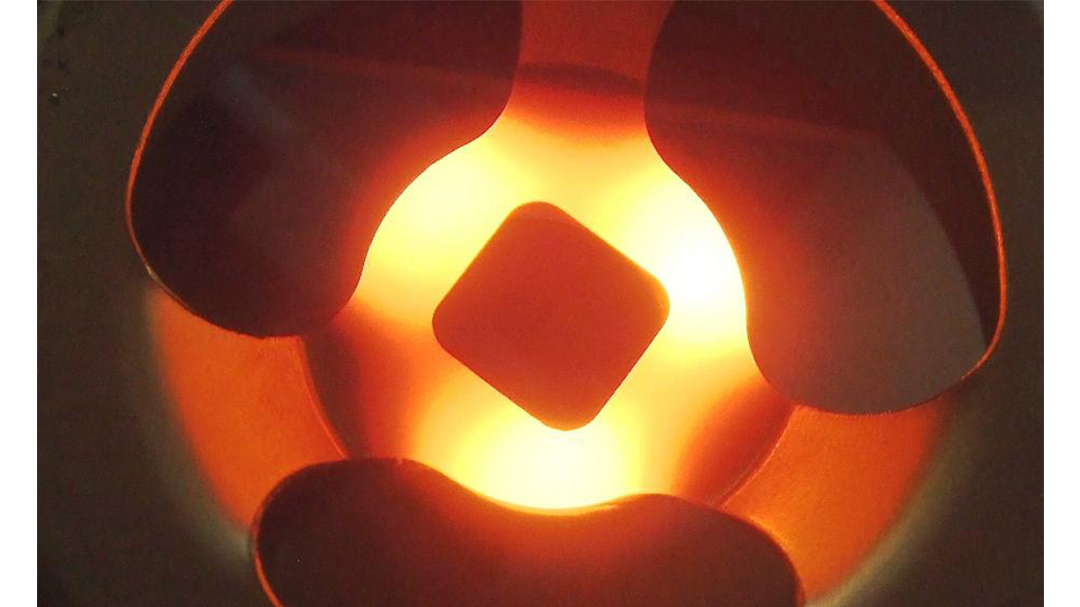
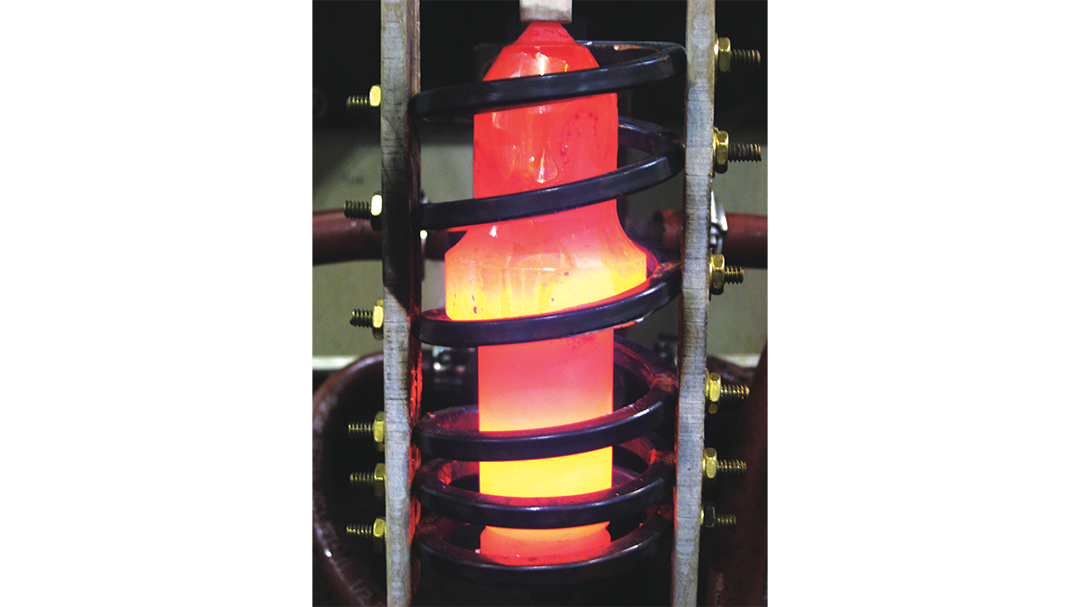
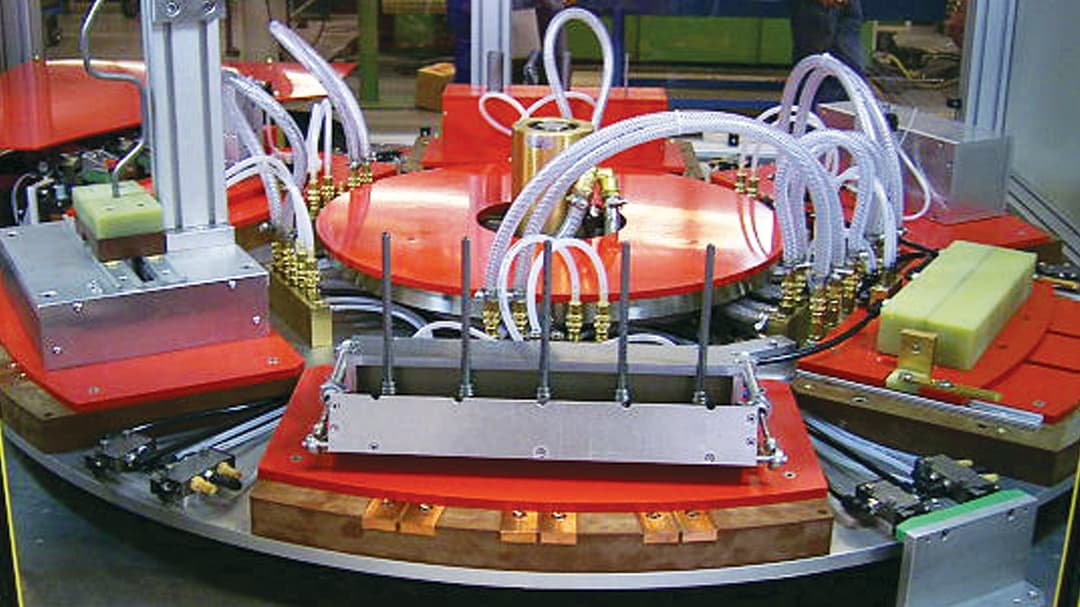
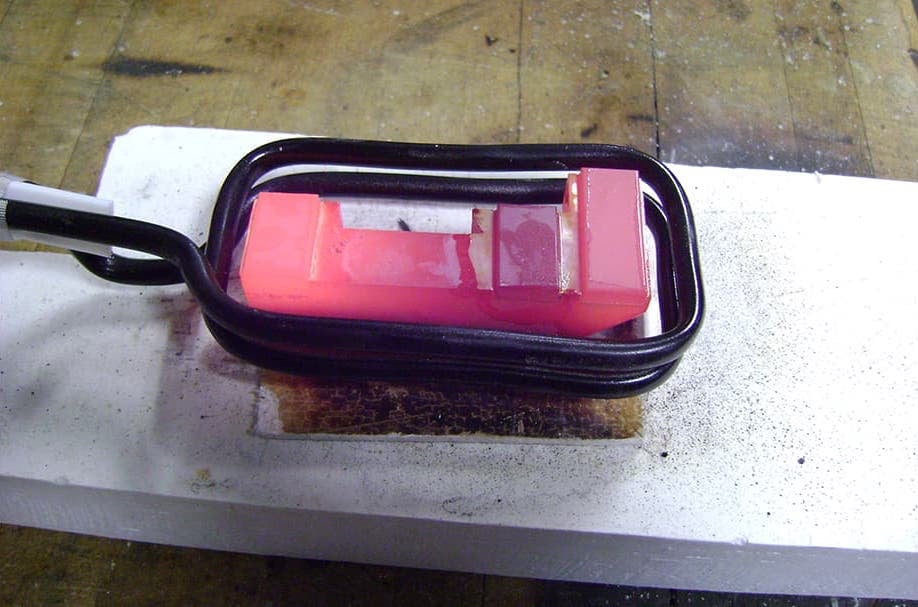
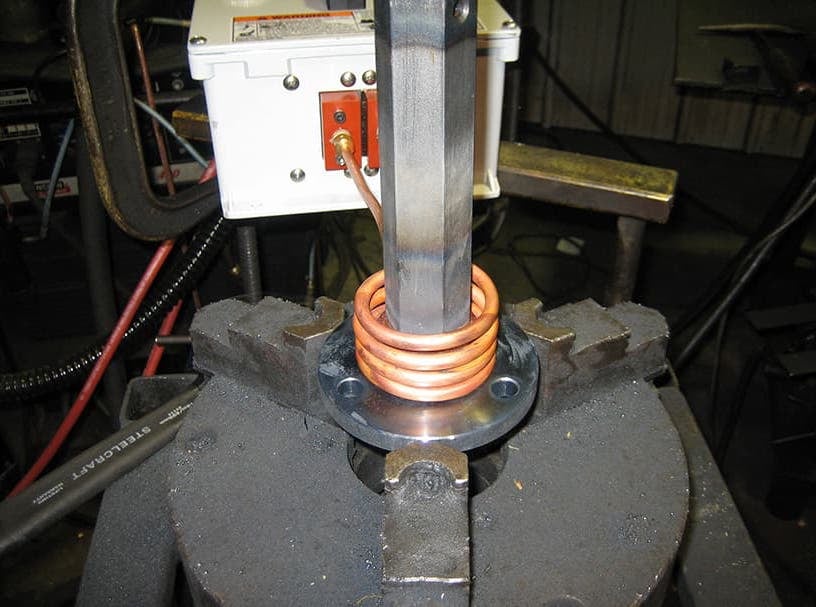
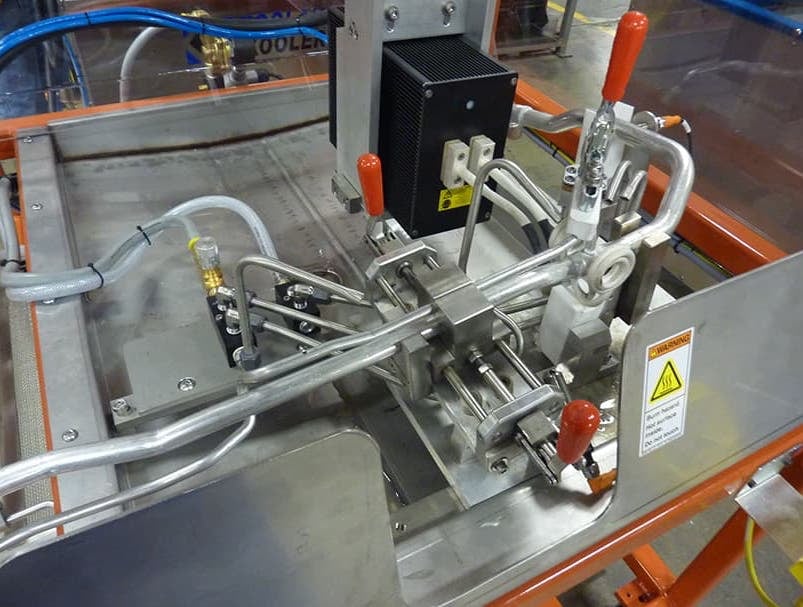
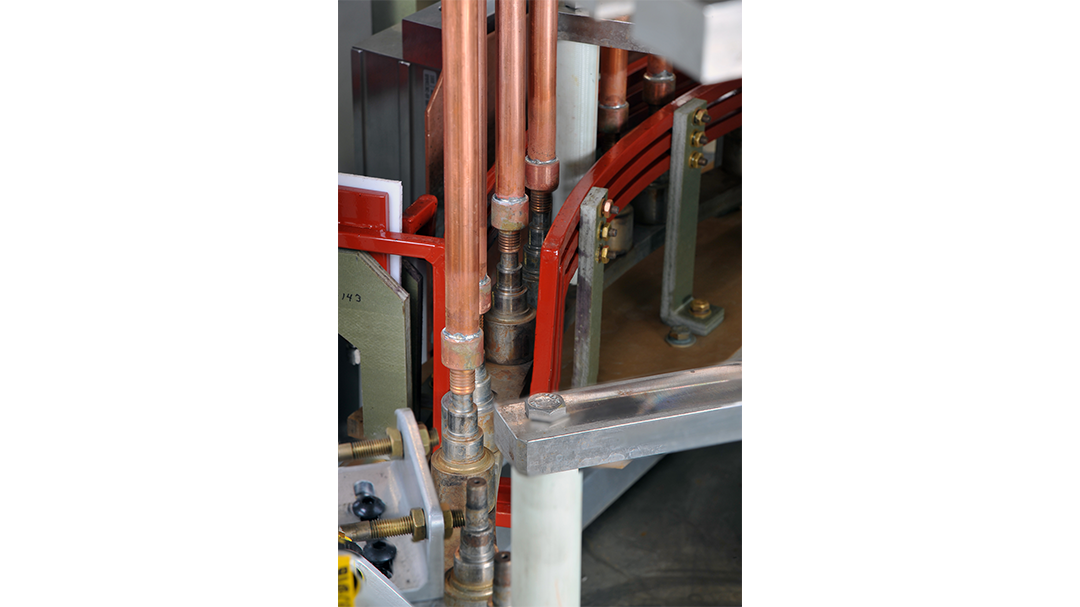
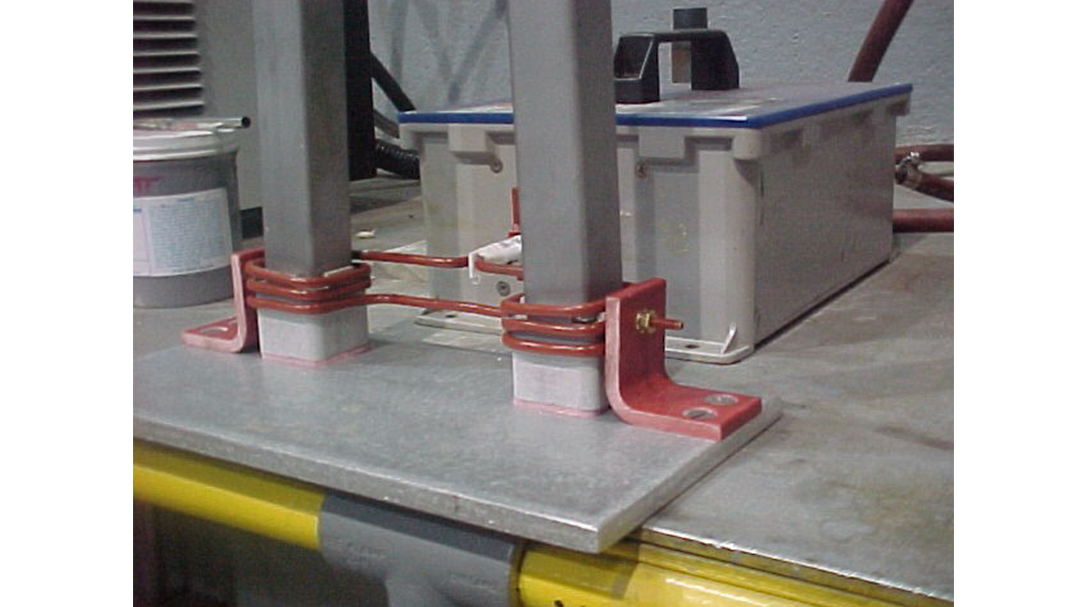
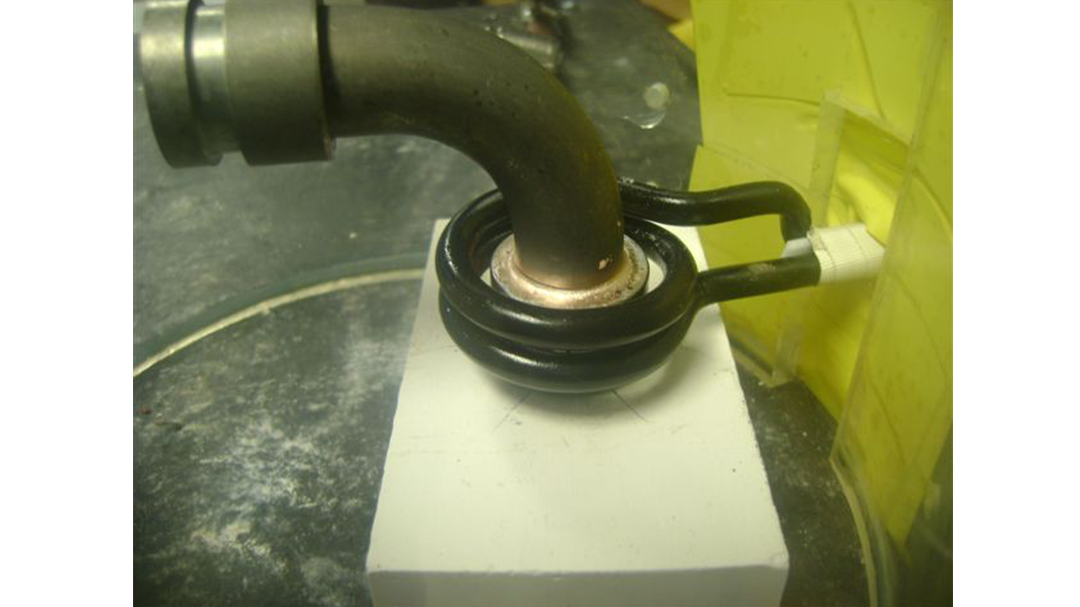
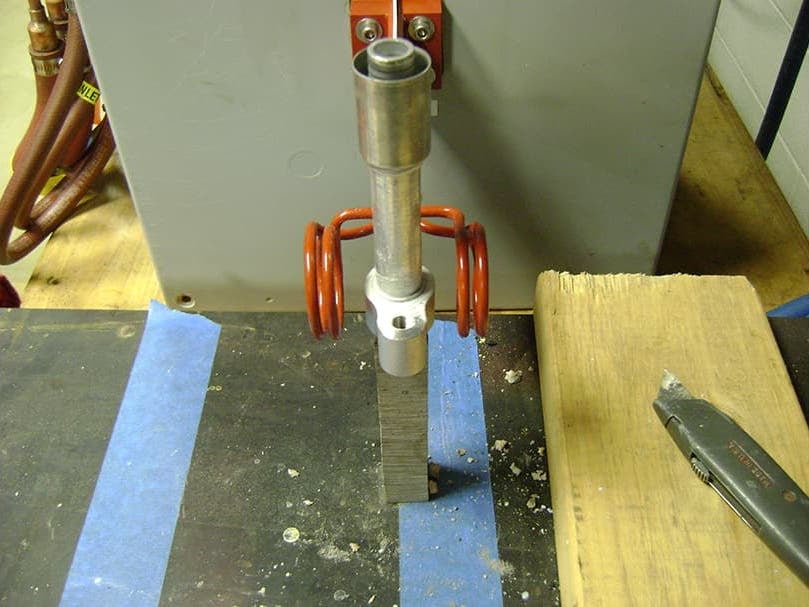
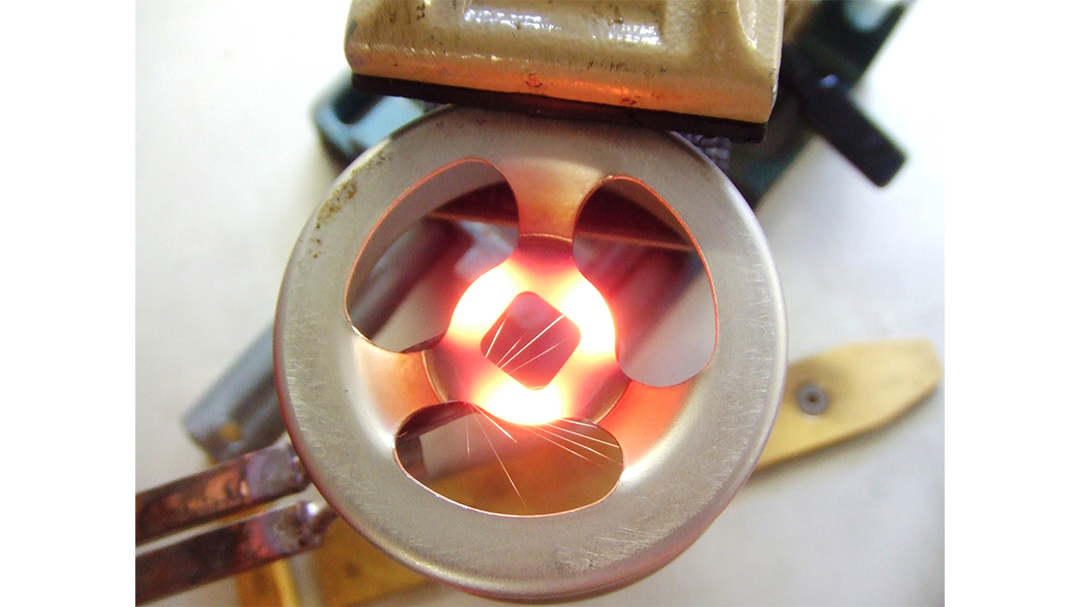
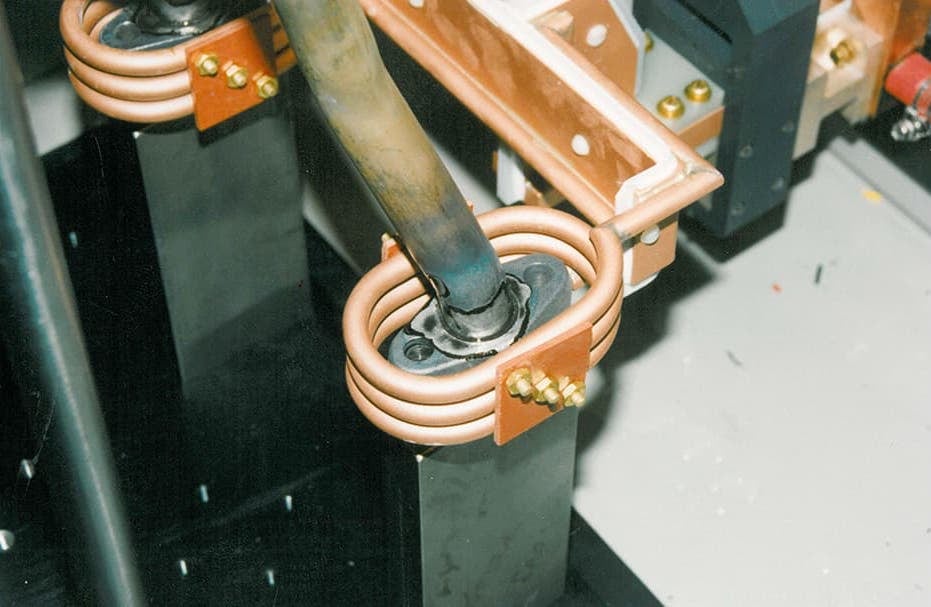
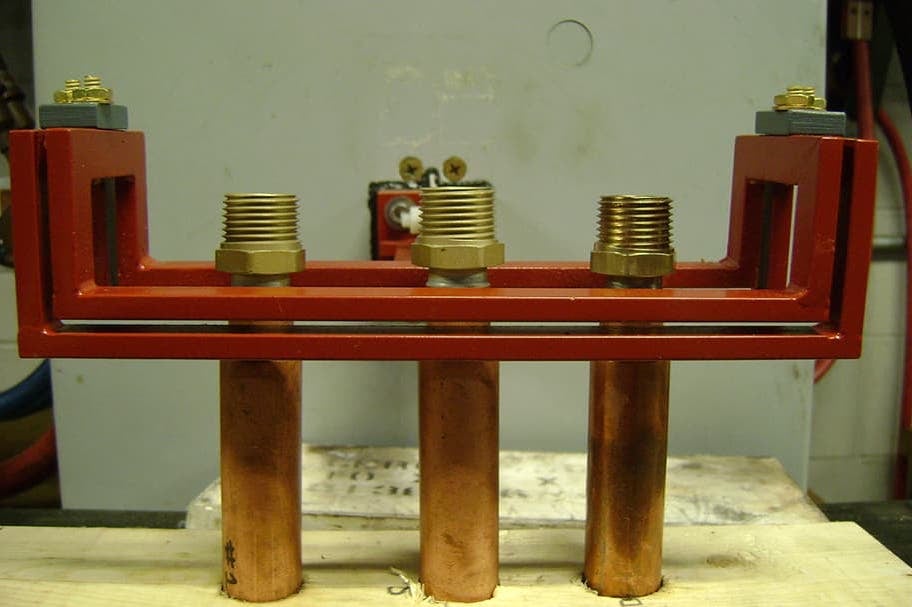
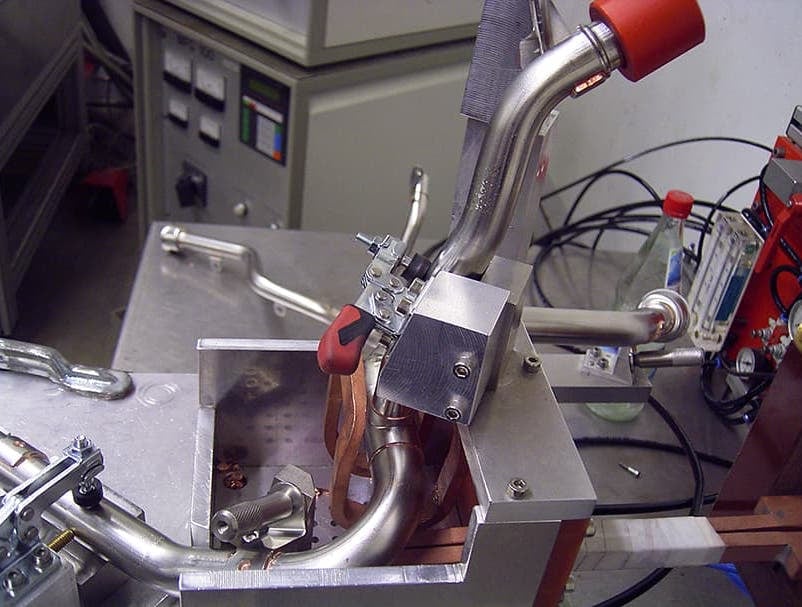
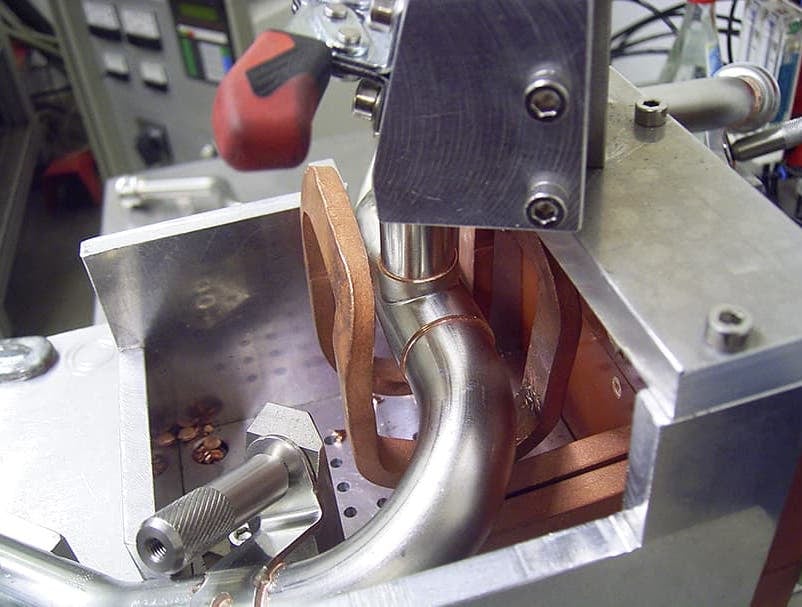
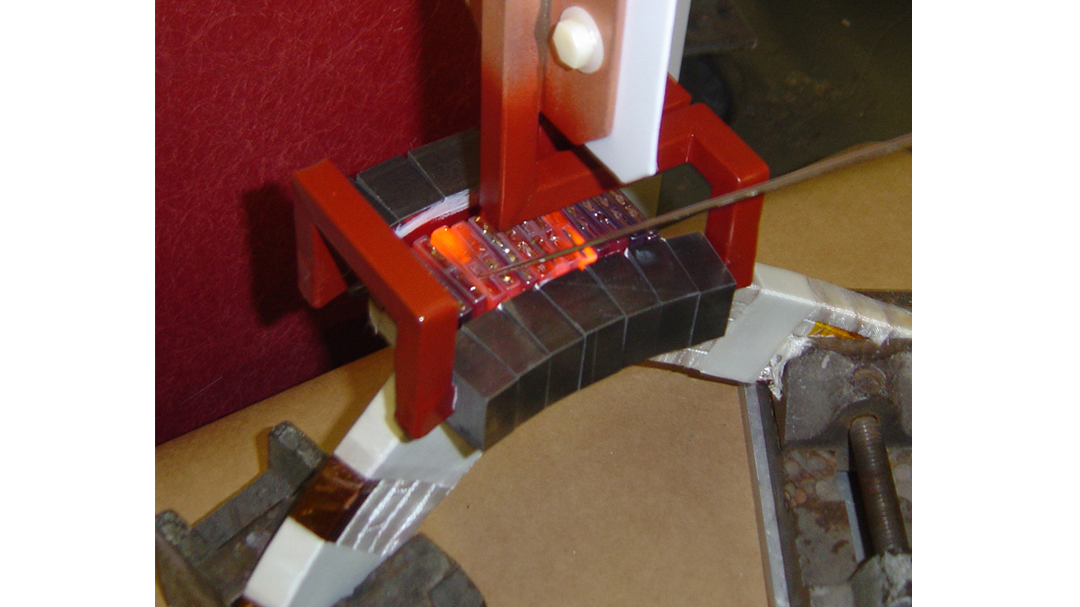
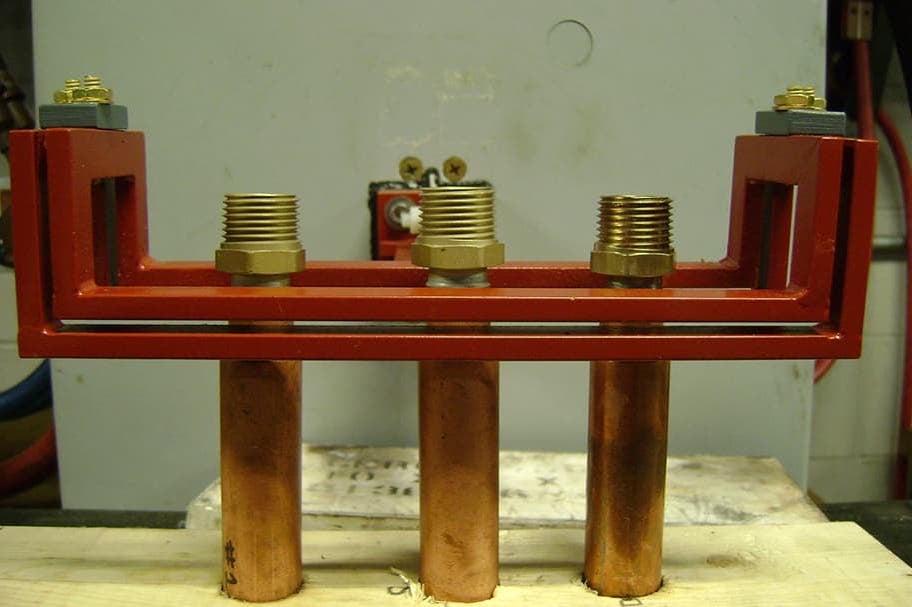
Induction Brazing Coil Design
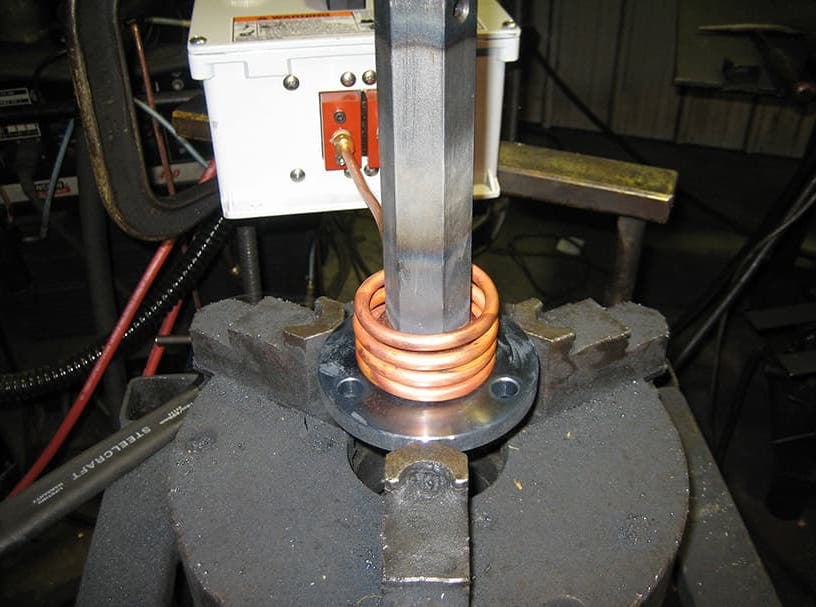
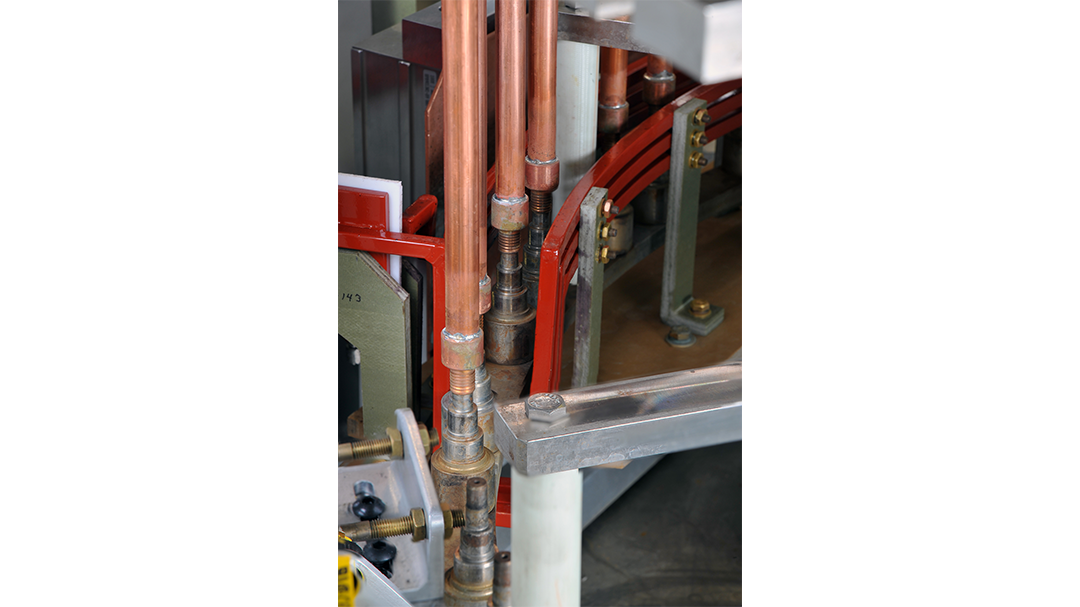
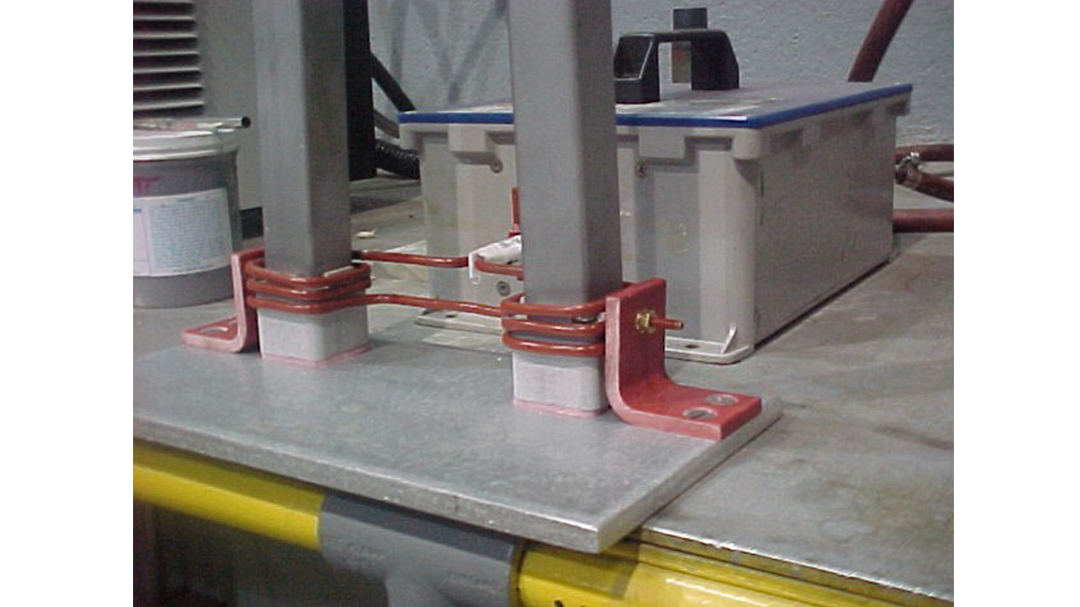
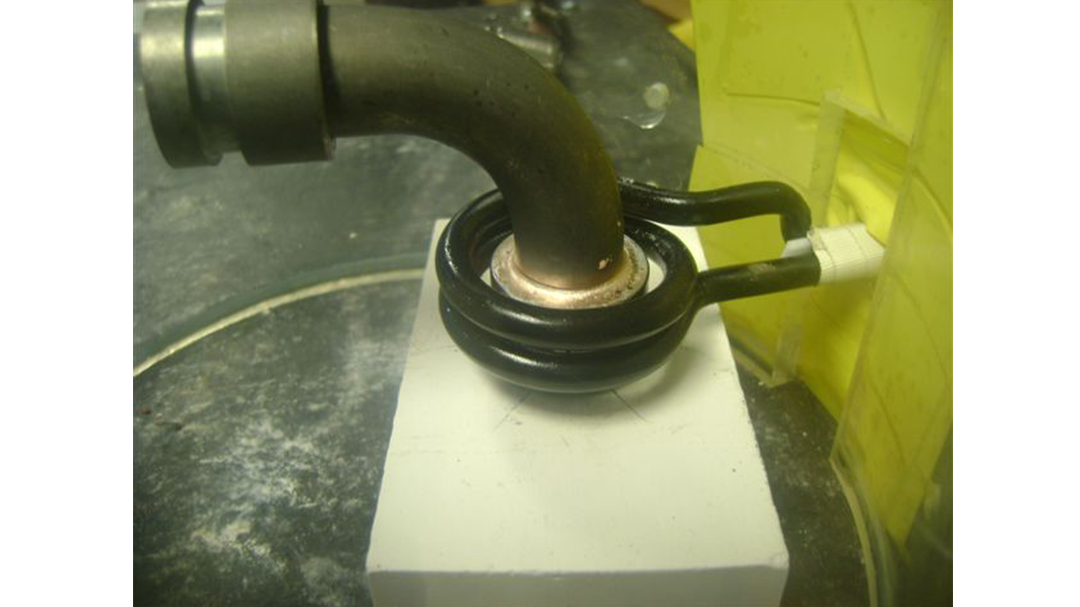
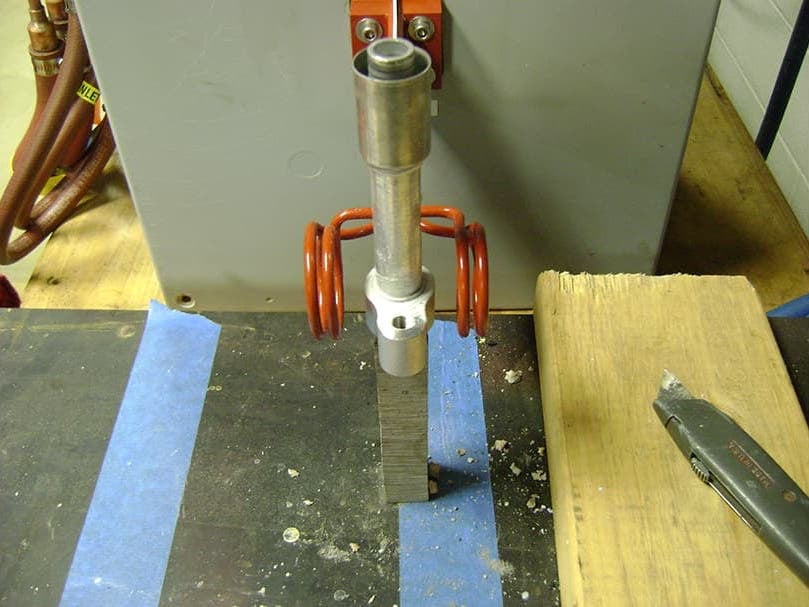
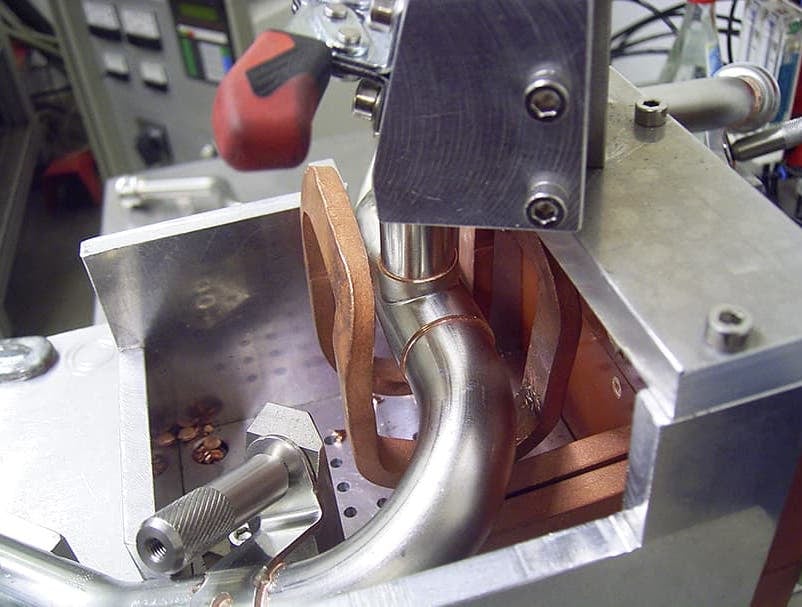
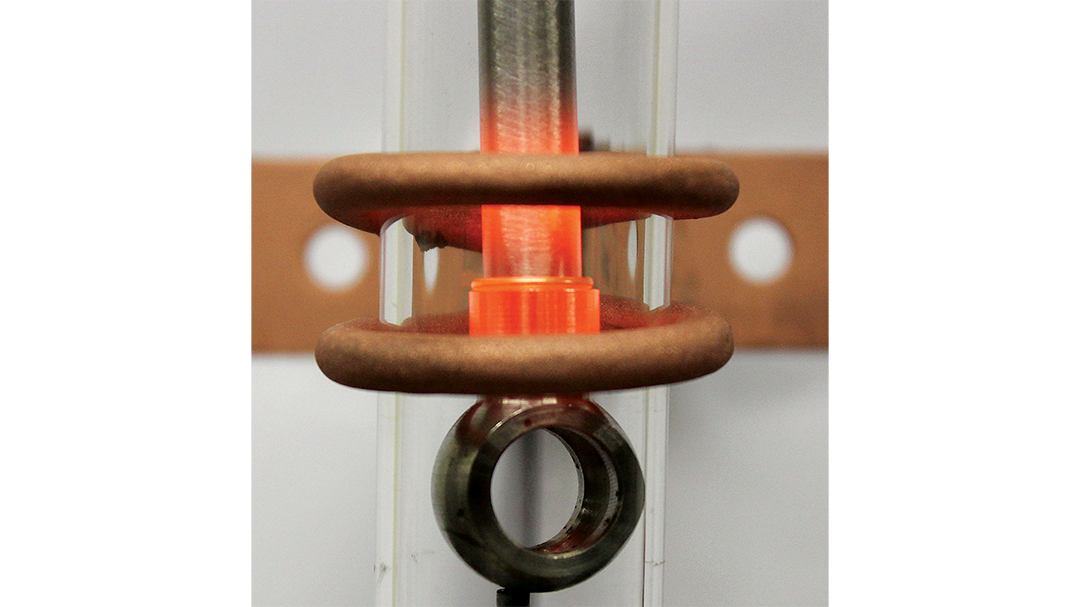
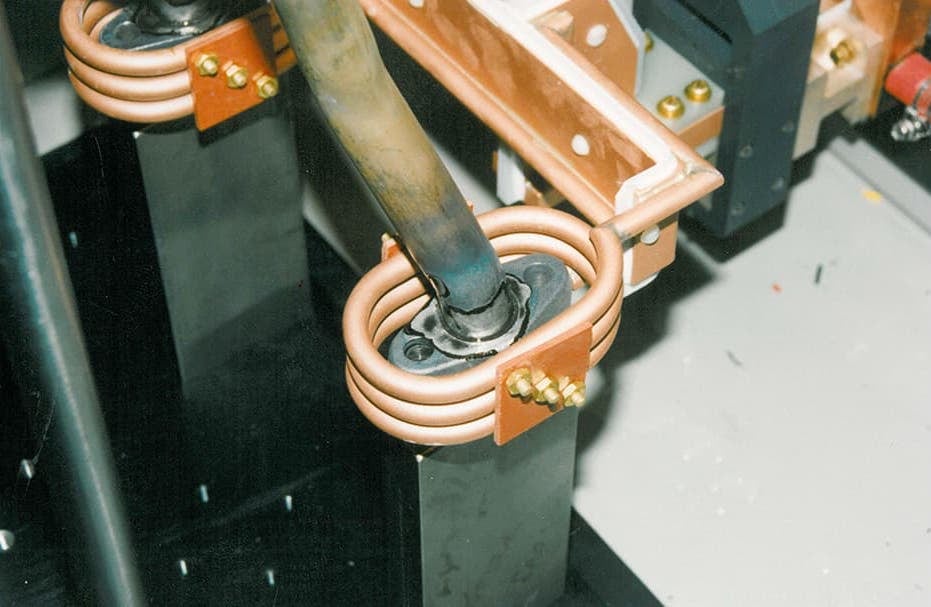
Fabricated from highly conductive copper tubing or plate, the induction coil’s design is influenced by the application, the selection of frequency, power density, and heat time. The purpose of the induction coil is to create a magnetic flux pattern to generate a current path in the work piece to selectively heat the area of the assembly to be brazed.
The coil must be correctly positioned on the assembly, allowing the required heating to be accomplished. The air gap or coupling space between the work piece and the inside of the coil should be minimized for reasons of efficiency. Typical design gaps of 0.125″ (3.175 mm) to 0.250″ (6.350 mm) are reasonable for brazing with a helical coil. Irregularly shaped sections may need additional clearances which require additional power to overcome these poor coupling efficiencies. These cases include situations where a round coil with a large air gap or a non-encircling coil is needed to access the braze area.
The area to be heated determines the length of the induction coil. An induction coil that is too short will require a longer heating time to allow the heat, by conduction, to cover the area. An induction coil that is too wide will heat more metal than necessary, and therefore be less efficient. Ajax TOCCO Magnethermic has many special designs of inductors for localized heating and coils that heat efficiently without surrounding the work piece.
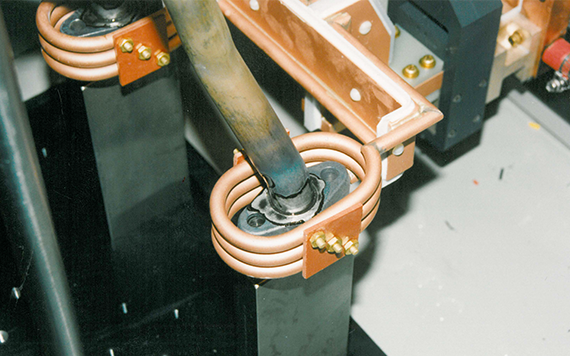
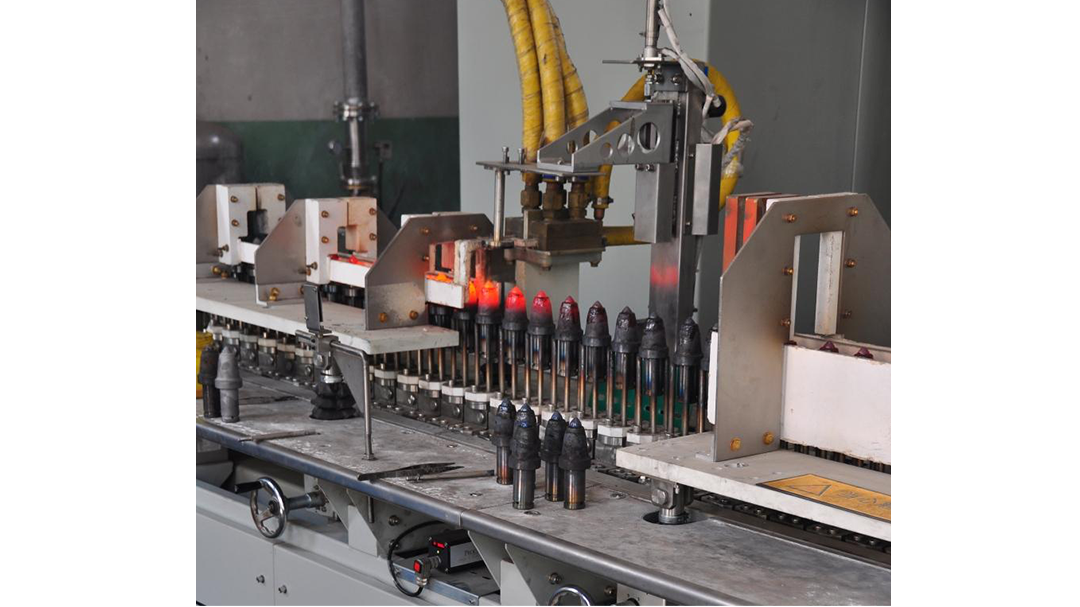
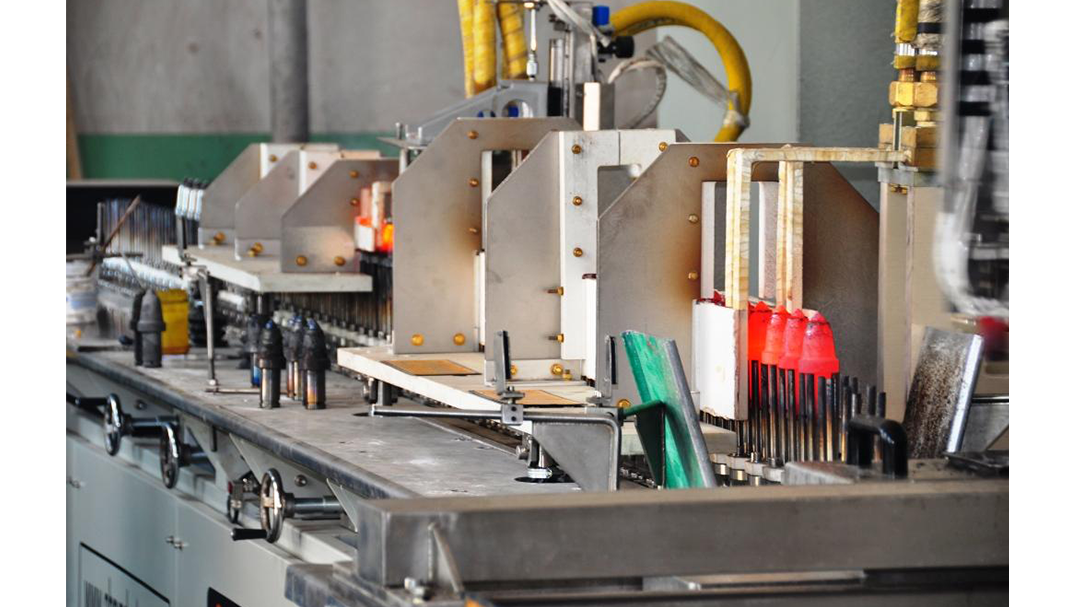
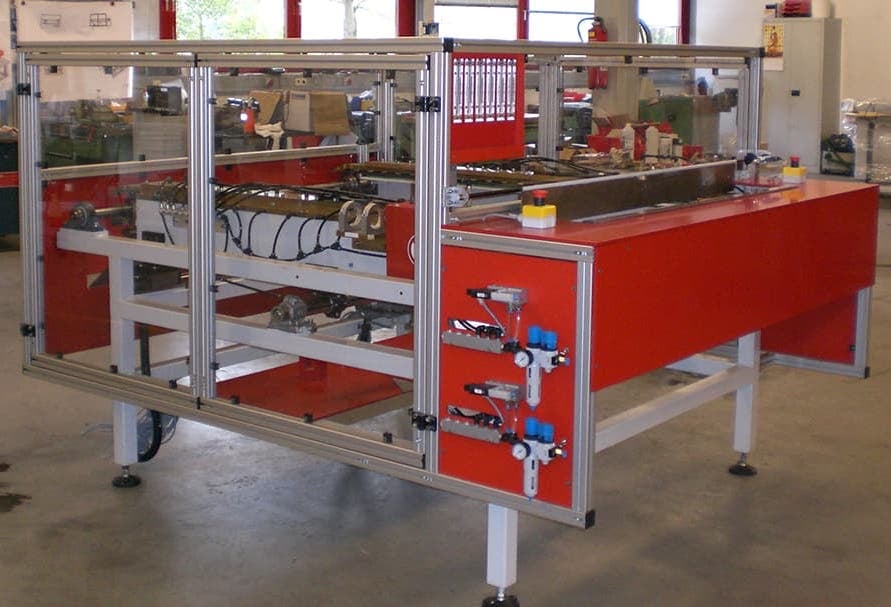
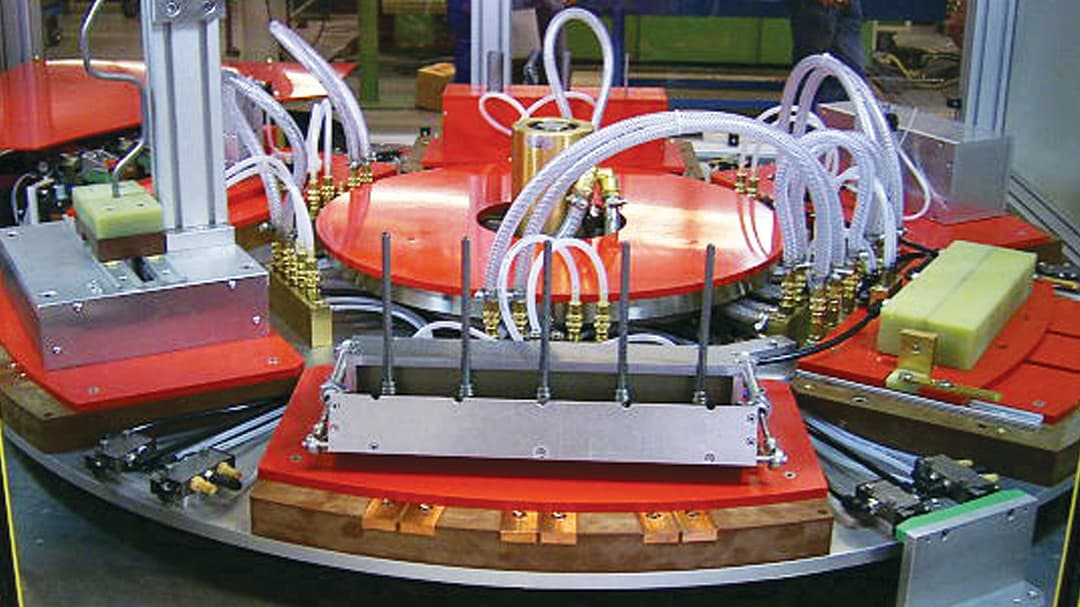
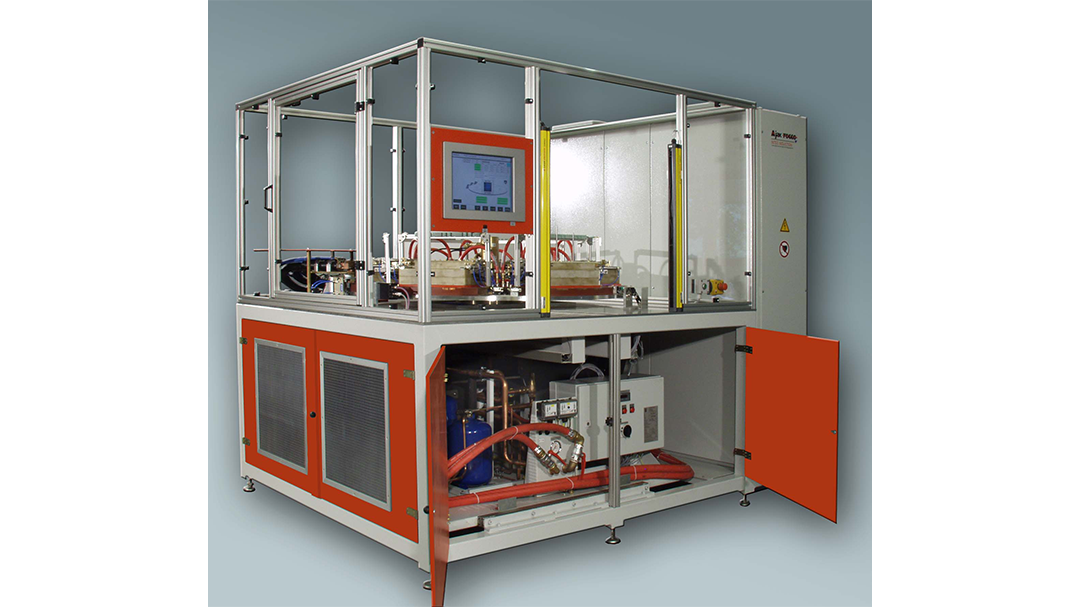
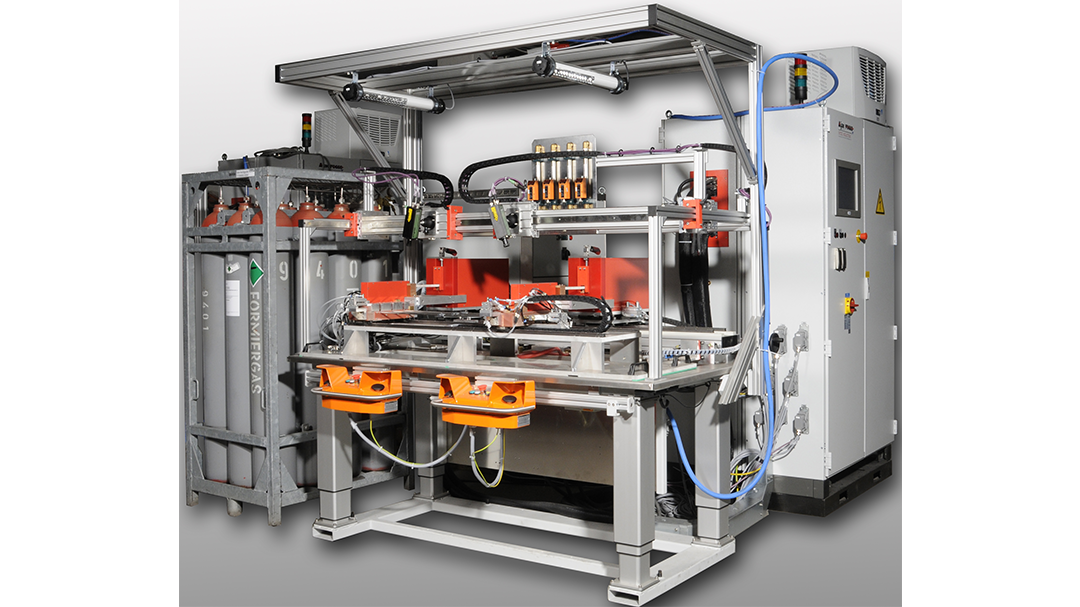
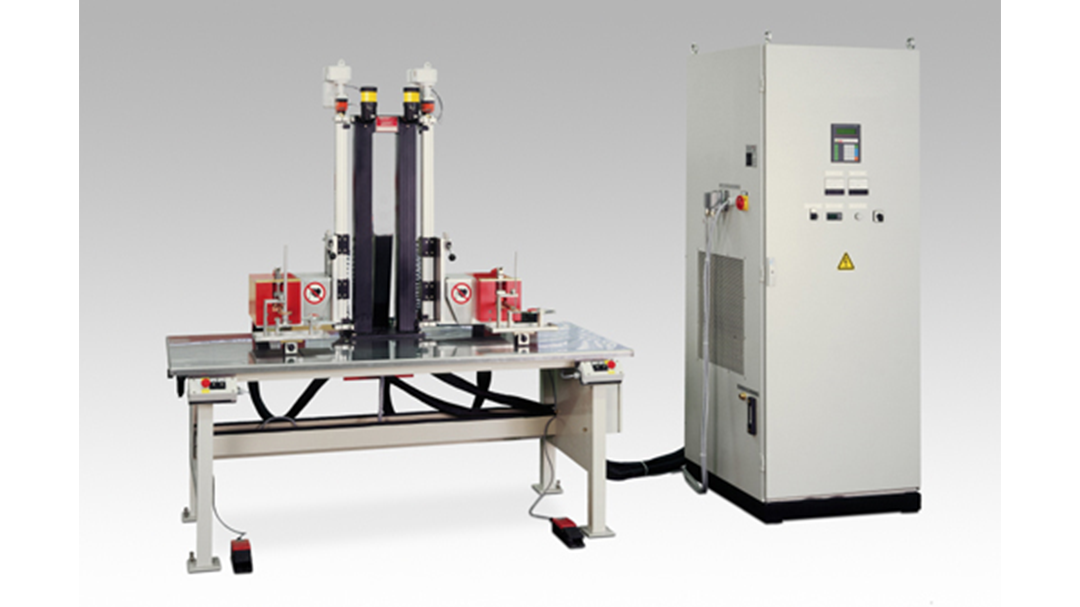
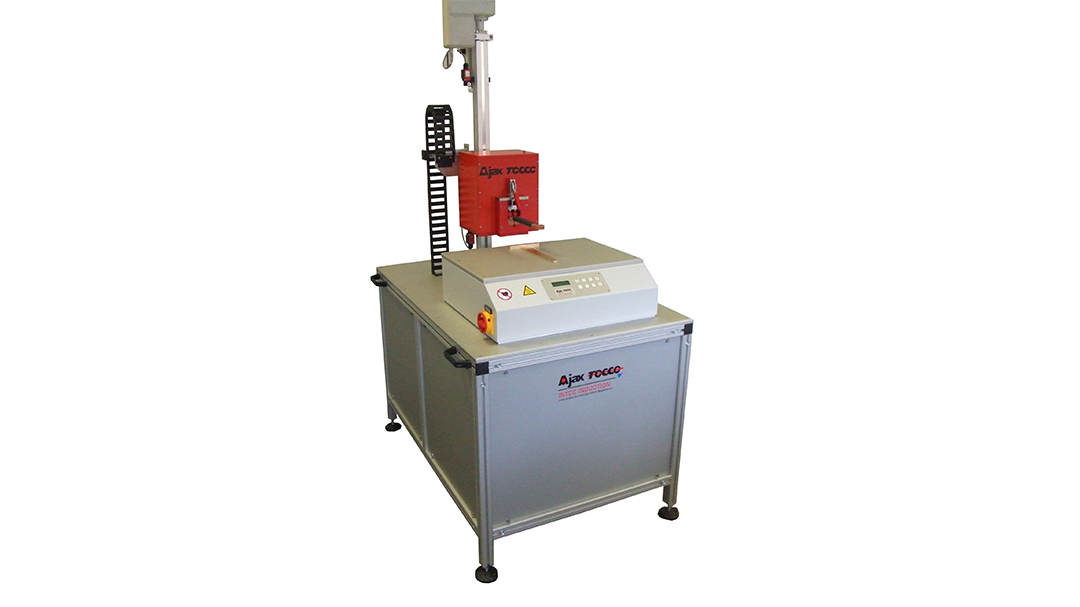
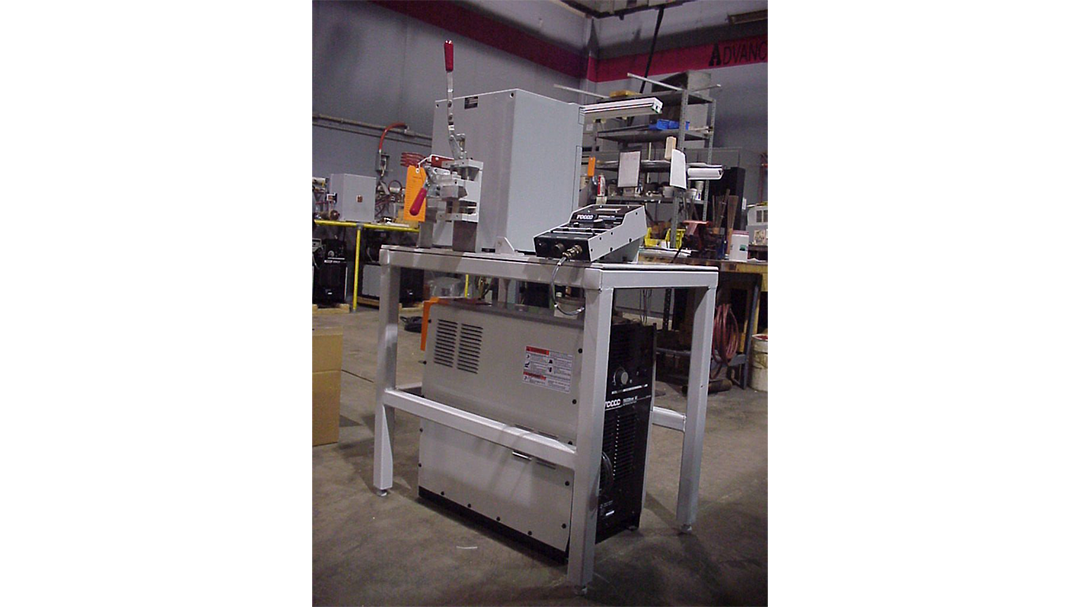
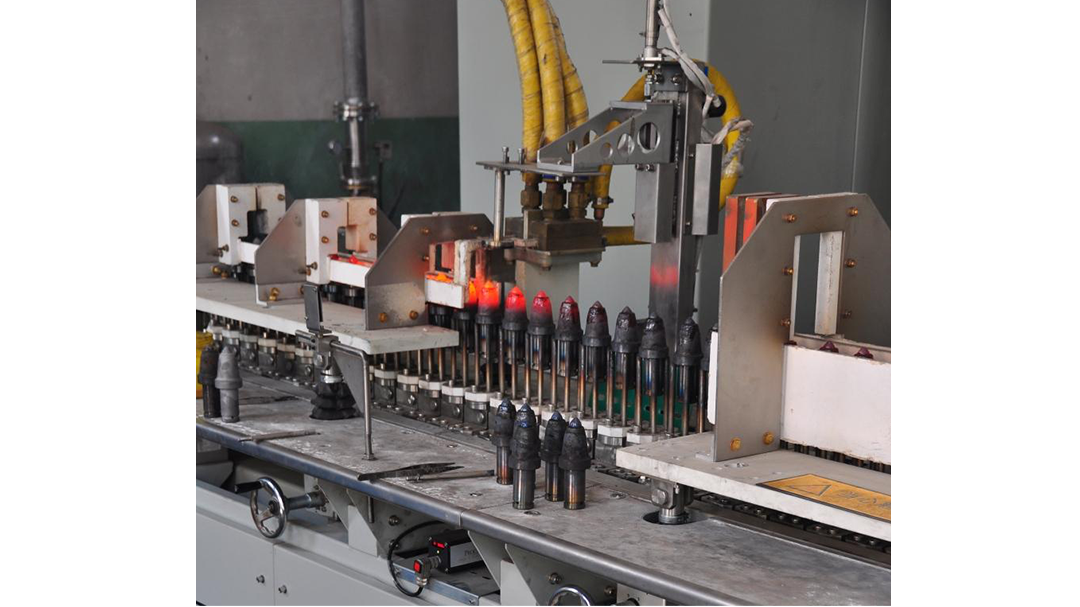
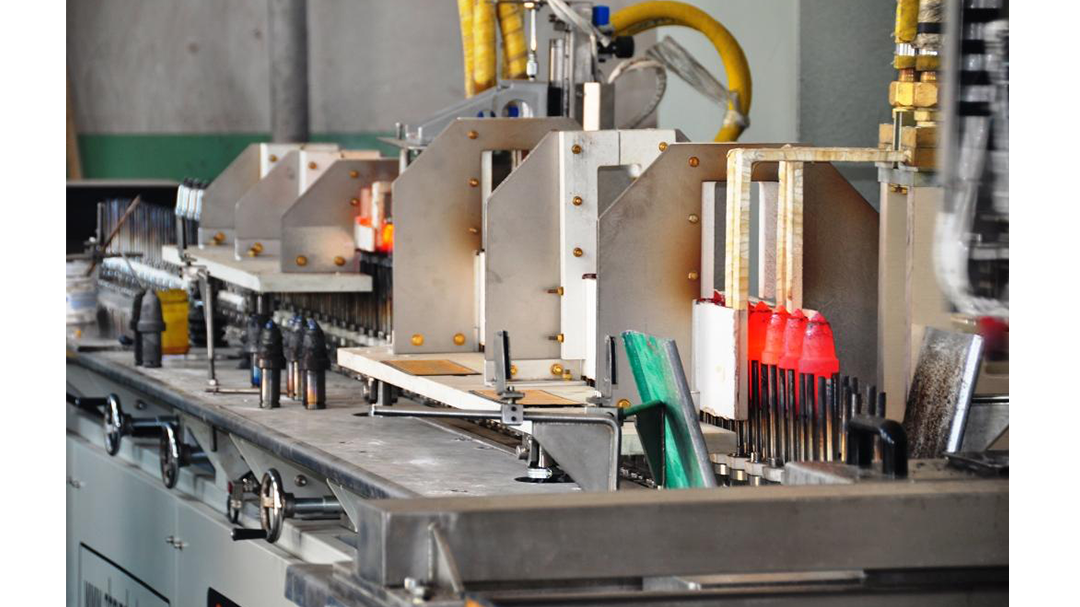
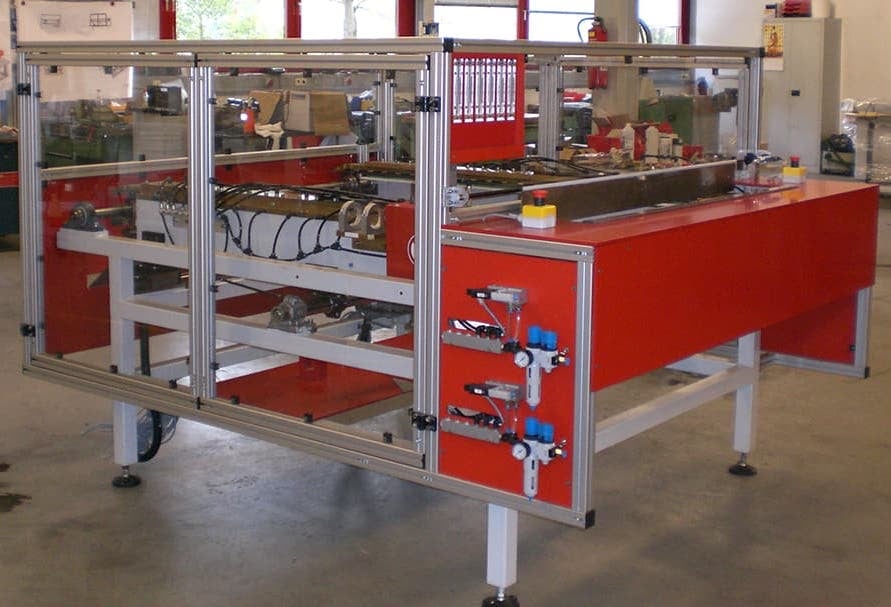
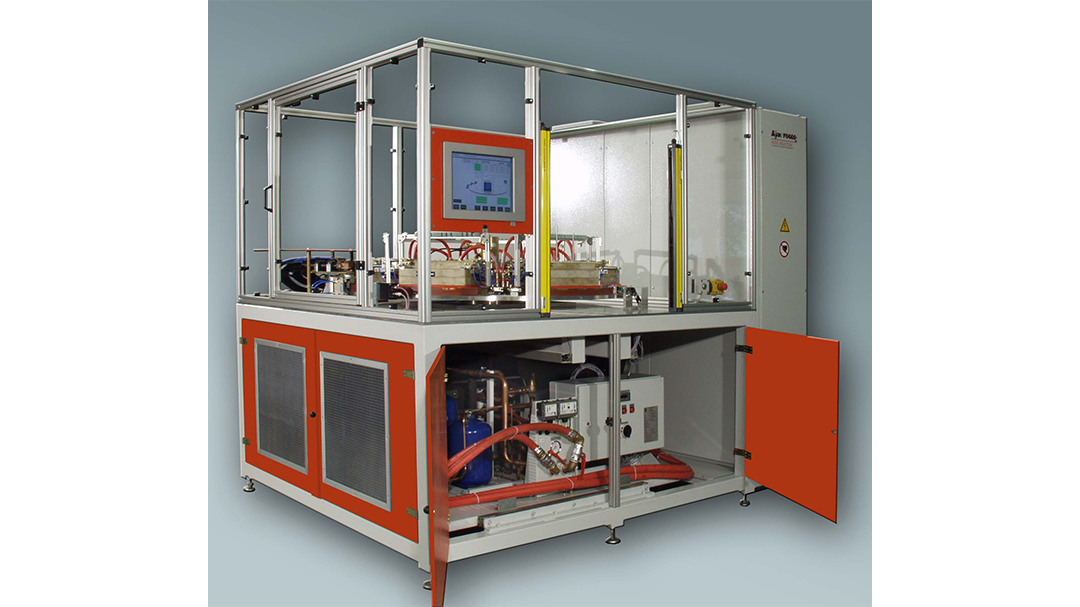
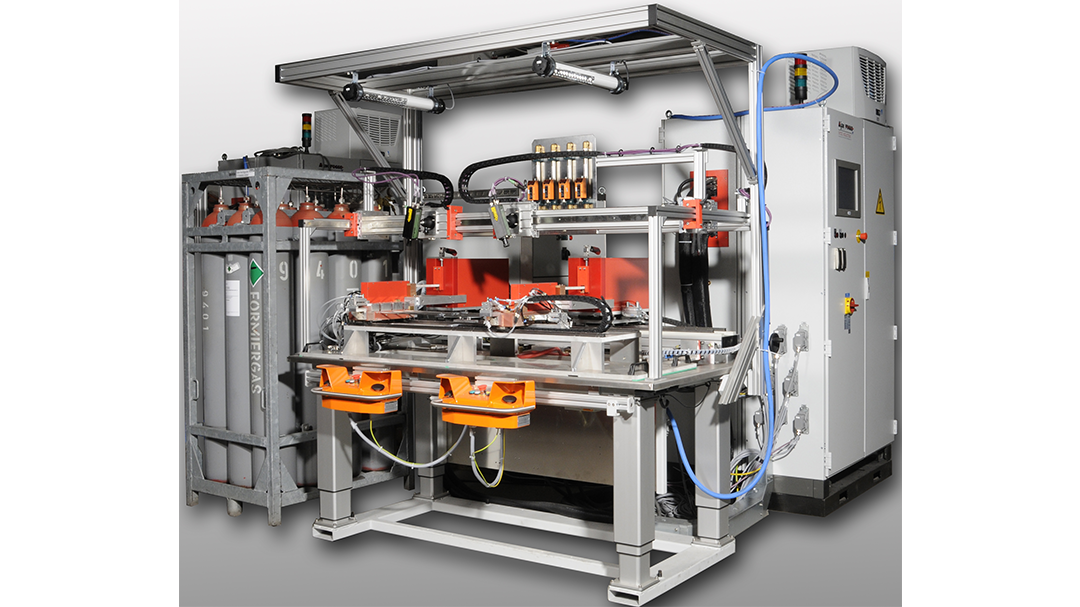
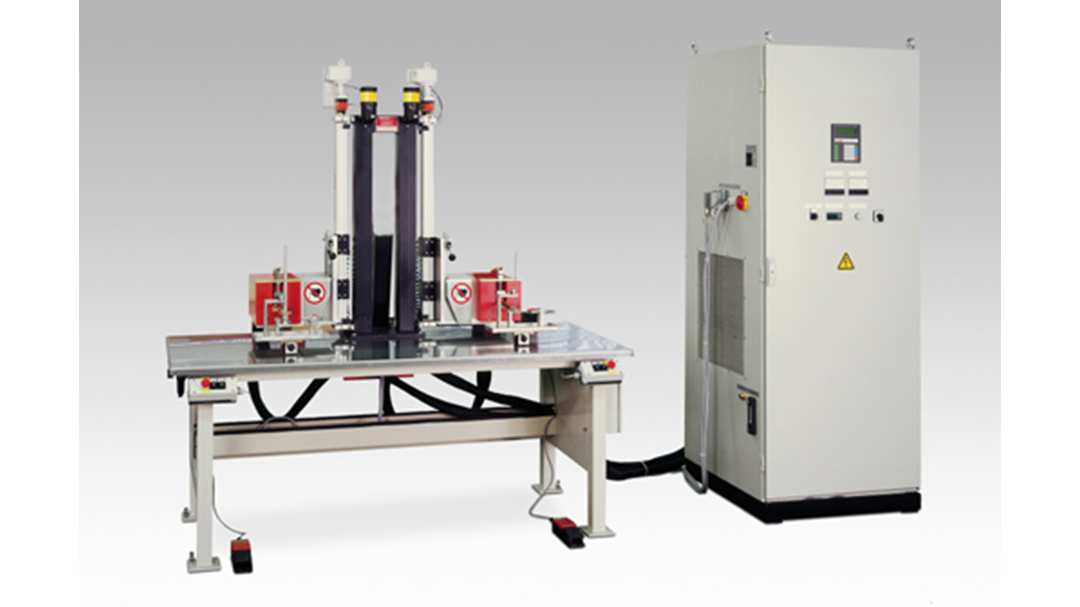
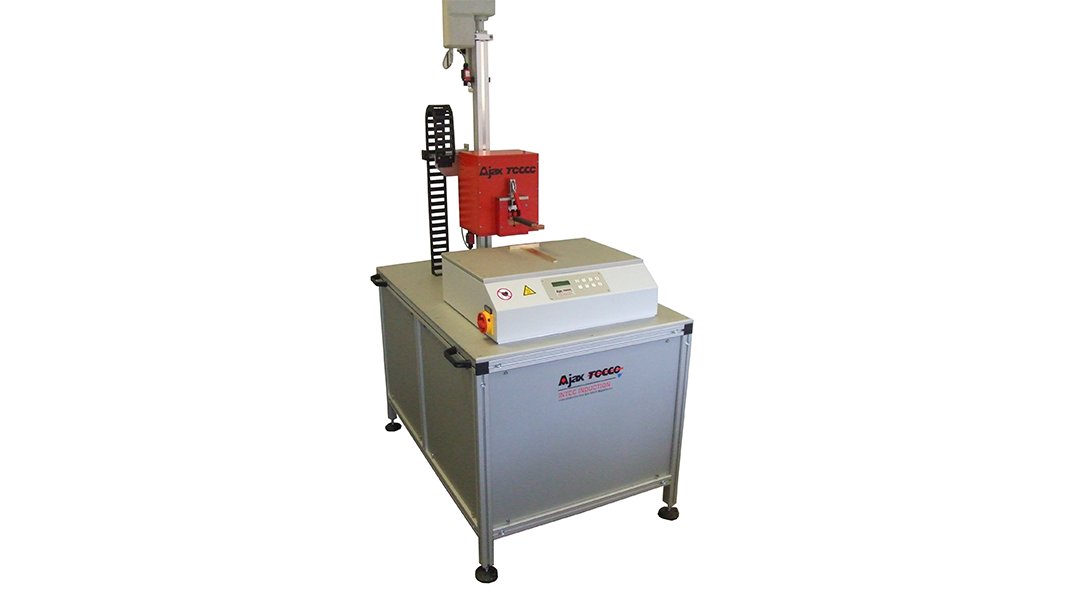
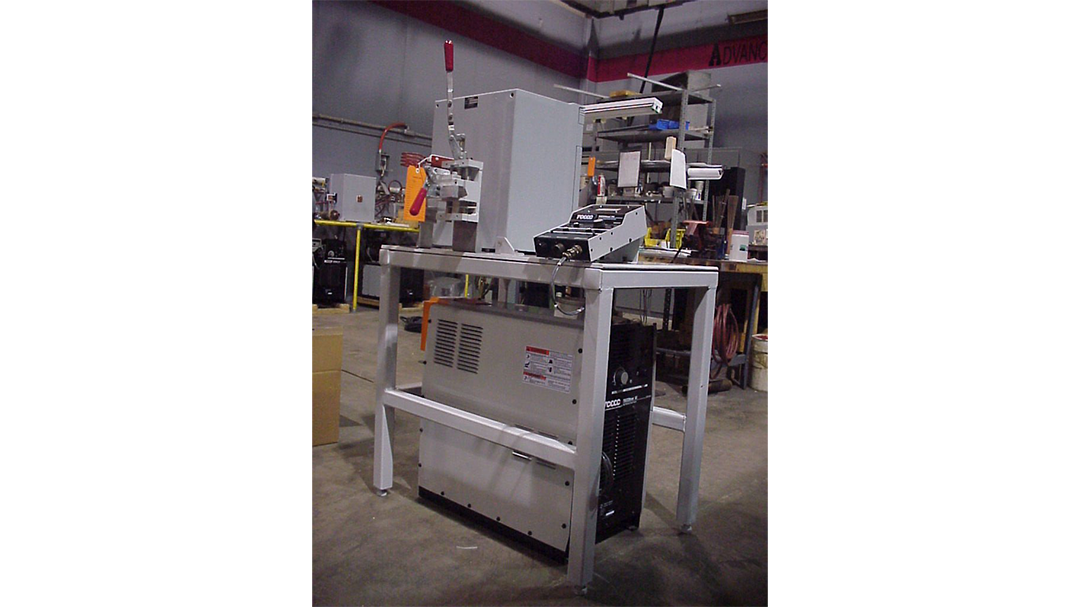
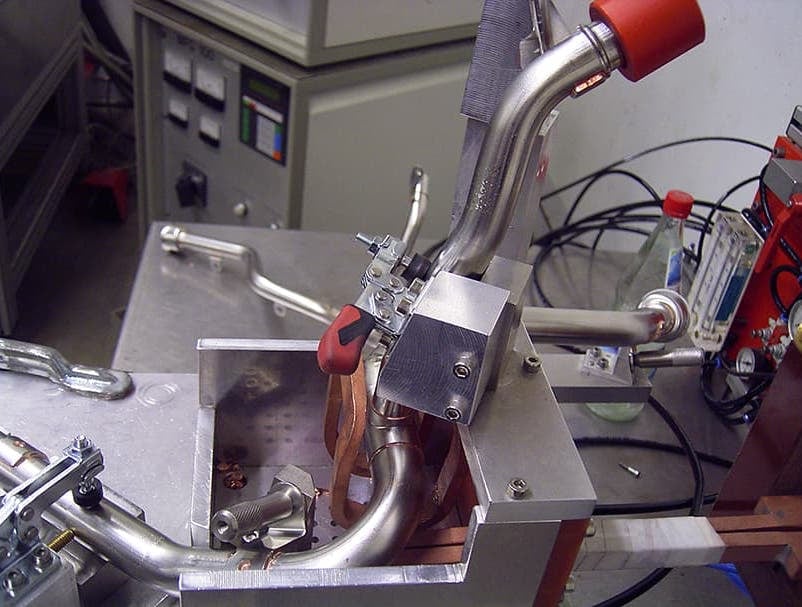
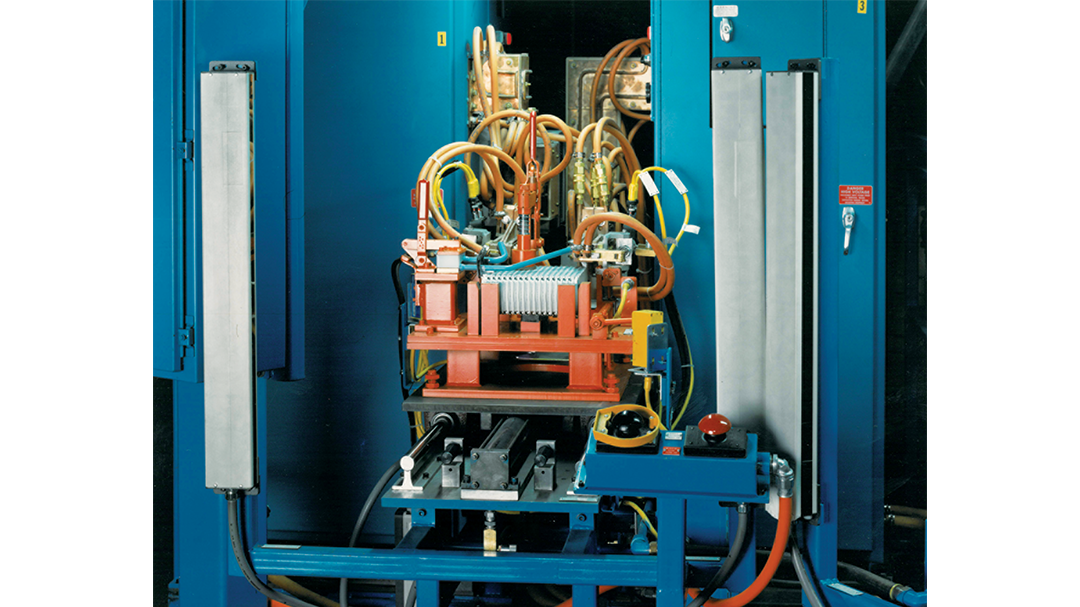
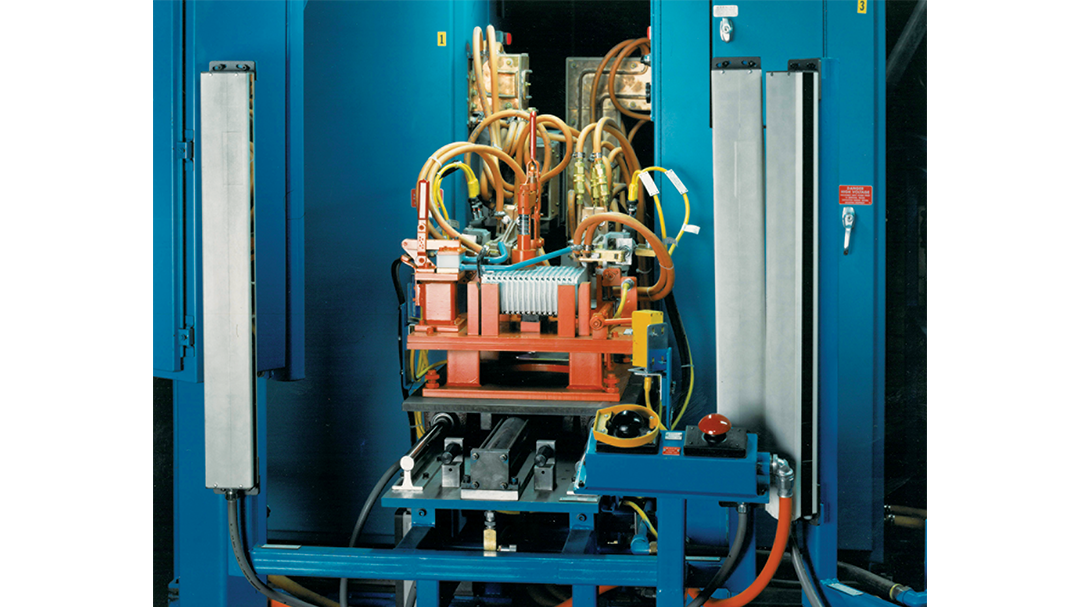
Induction Brazing Systems
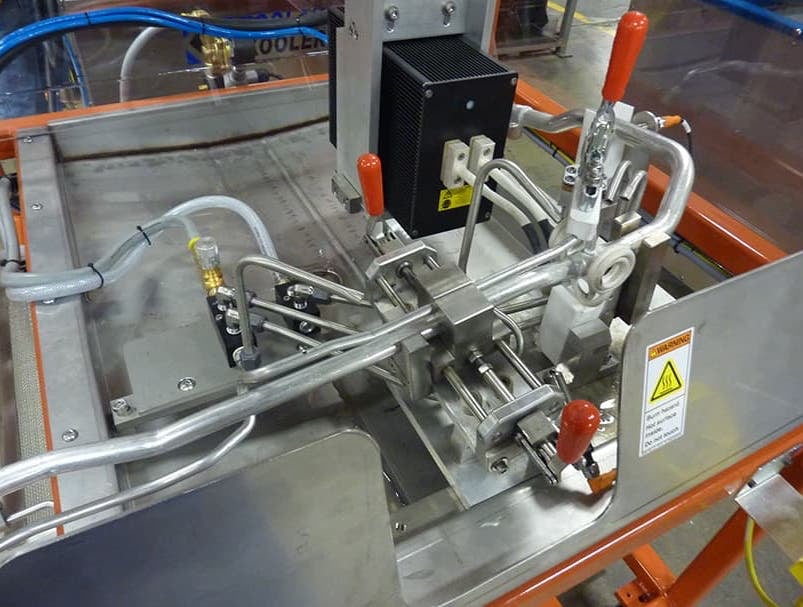
Ajax TOCCO can provide standard and custom equipment. From stand-alone, inline, rotary, indexing, or continuous, our team of application and process engineers has the capability and experience to give you the best system for your production needs. We offer manual load, automation, multi-station, tabletop systems, fluxless brazing, and even controlled atmosphere options.

Resources
Thank you for requesting access to this brochure.
You can access your download by clicking here.




